More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

MAJESTY AliNICOLE WOW!
3 years ago
YouTube's faceless videos are growing in popularity, but this is nothing new.
I've always bucked social media norms. YouTube doesn't compare. Traditional video made me zig when everyone zagged. Audio, picture personality animation, thought movies, and slide show videos are most popular and profitable.

YouTube's business is shifting. While most video experts swear by the idea that YouTube success is all about making personal and professional Face-Share-Videos, those who use YouTube for business know things are different.
In this article, I will share concepts from my mini master class Figures to Followers: Prioritizing Purposeful Profits Over Popularity on YouTube to Create the Win-Win for You, Your Audience & More and my forthcoming publication The WOWTUBE-PRENEUR FACTOR EVOLUTION: The Basics of Powerfully & Profitably Positioning Yourself as a Video Communications Authority to Broadcast Your WOW Effect as a Video Entrepreneur.
I've researched the psychology, anthropology, and anatomy of significant social media platforms as an entrepreneur and social media marketing expert. While building my YouTube empire, I've paid particular attention to what works for short, mid, and long-term success, whether it's a niche-focused, lifestyle, or multi-interest channel.
Most new, semi-new, and seasoned YouTubers feel vlog-style or live-on-camera videos are popular. Faceless, animated, music-text-based, and slideshow videos do well for businesses.
Buyer-consumer vs. content-consumer thinking is totally different when absorbing content. Profitability and popularity are closely related, however most people become popular with traditional means but not profitable.
In my experience, Faceless videos are more profitable, although it depends on the channel's style. Several professionals are now teaching in their courses that non-traditional films are making the difference in their business success and popularity.
Face-Share-Personal-Touch videos make audiences feel like they know the personality, but they're not profitable.
Most spend hours creating articles, videos, and thumbnails to seem good. That's how most YouTubers gained their success in the past, but not anymore.
Looking the part and performing a typical role in videos doesn't convert well, especially for newbie channels.
Working with video marketers and YouTubers for years, I've noticed that most struggle to be consistent with content publishing since they exclusively use formats that need extensive development. Camera and green screen set ups, shooting/filming, and editing for post productions require their time, making it less appealing to post consistently, especially if they're doing all the work themselves.
Because they won't make simple format videos or audio videos with an overlay image, they overcomplicate the procedure (even with YouTube Shorts), and they leave their channels for weeks or months. Again, they believe YouTube only allows specific types of videos. Even though this procedure isn't working, they plan to keep at it.

A successful YouTube channel needs multiple video formats to suit viewer needs, I teach. Face-Share-Personal Touch and Faceless videos are both useful.
How people engage with YouTube content has changed over the years, and the average customer is no longer interested in an all-video channel.
Face-Share-Personal-Touch videos are great
Google Live
Online training
Giving listeners a different way to access your podcast that is being broadcast on sites like Anchor, BlogTalkRadio, Spreaker, Google, Apple Store, and others Many people enjoy using a video camera to record themselves while performing the internet radio, Facebook, or Instagram Live versions of their podcasts.
Video Blog Updates
even more
Faceless videos are popular for business and benefit both entrepreneurs and audiences.
For the business owner/entrepreneur…
Less production time results in time dollar savings.
enables the business owner to demonstrate the diversity of content development
For the Audience…
The channel offers a variety of appealing content options.
The same format is not monotonous or overly repetitive for the viewers.
Below are a couple videos from YouTube guru Make Money Matt's channel, which has over 347K subscribers.
Enjoy
24 Best Niches to Make Money on YouTube Without Showing Your Face
Make Money on YouTube Without Making Videos (Free Course)
In conclusion, you have everything it takes to build your own YouTube brand and empire. Learn the rules, then adapt them to succeed.
Please reread this and the other suggested articles for optimal benefit.
I hope this helped. How has this article helped you? Follow me for more articles like this and more multi-mission expressions.

The woman
3 years ago
Because he worked on his side projects during working hours, my junior was fired and sued.
Many developers do it, but I don't approve.

Aren't many programmers part-time? Many work full-time but also freelance. If the job agreement allows it, I see no problem.
Tech businesses' policies vary. I have a friend in Google, Germany. According to his contract, he couldn't do an outside job. Google owns any code he writes while employed.
I was shocked. Later, I found that different Google regions have different policies.
A corporation can normally establish any agreement before hiring you. They're negotiable. When there's no agreement, state law may apply. In court, law isn't so simple.
I won't delve into legal details. Instead, let’s talk about the incident.
How he was discovered
In one month, he missed two deadlines. His boss was frustrated because the assignment wasn't difficult to miss twice. When a team can't finish work on time, they all earn bad grades.
He annoyed the whole team. One team member (anonymous) told the project manager he worked on side projects during office hours. He may have missed deadlines because of this.
The project manager was furious. He needed evidence. The manager caught him within a week. The manager told higher-ups immediately.
The company wanted to set an example
Management could terminate him and settle the problem. But the company wanted to set an example for those developers who breached the regulation.
Because dismissal isn't enough. Every organization invests heavily in developer hiring. If developers depart or are fired after a few months, the company suffers.
The developer spent 10 months there. The employer sacked him and demanded ten months' pay. Or they'd sue him.
It was illegal and unethical. The youngster paid the fine and left the company quietly to protect his career.
Right or wrong?
Is the developer's behavior acceptable? Let's discuss developer malpractice.
During office hours, may developers work on other projects? If they're bored during office hours, they might not. Check the employment contract or state law.
If there's no employment clause, check country/state law. Because you can't justify breaking the law. Always. Most employers own their employees' work hours unless it's a contractual position.
If the company agrees, it's fine.
I also oppose companies that force developers to work overtime without pay.
Most states and countries have laws that help companies and workers. Law supports employers in this case. If any of the following are true, the company/employer owns the IP under California law.
using the business's resources
any equipment, including a laptop used for business.
company's mobile device.
offices of the company.
business time as well. This is crucial. Because this occurred in the instance of my junior.
Company resources are dangerous. Because your company may own the product's IP. If you have seen the TV show Silicon Valley, you have seen a similar situation there, right?
Conclusion
Simple rule. I avoid big side projects. I work on my laptop on weekends for side projects. I'm safe. But I also know that my company might not be happy with that.
As an employee, I suppose I can. I can make side money. I won't promote it, but I'll respect their time, resources, and task. I also sometimes work extra time to finish my company’s deadlines.

Thomas Tcheudjio
3 years ago
If you don't crush these 3 metrics, skip the Series A.
I recently wrote about getting VCs excited about Marketplace start-ups. SaaS founders became envious!
Understanding how people wire tens of millions is the only Series A hack I recommend.
Few people understand the intellectual process behind investing.
VC is risk management.
Series A-focused VCs must cover two risks.
1. Market risk
You need a large market to cross a threshold beyond which you can build defensibilities. Series A VCs underwrite market risk.
They must see you have reached product-market fit (PMF) in a large total addressable market (TAM).
2. Execution risk
When evaluating your growth engine's blitzscaling ability, execution risk arises.
When investors remove operational uncertainty, they profit.
Series A VCs like businesses with derisked revenue streams. Don't raise unless you have a predictable model, pipeline, and growth.
Please beat these 3 metrics before Series A:
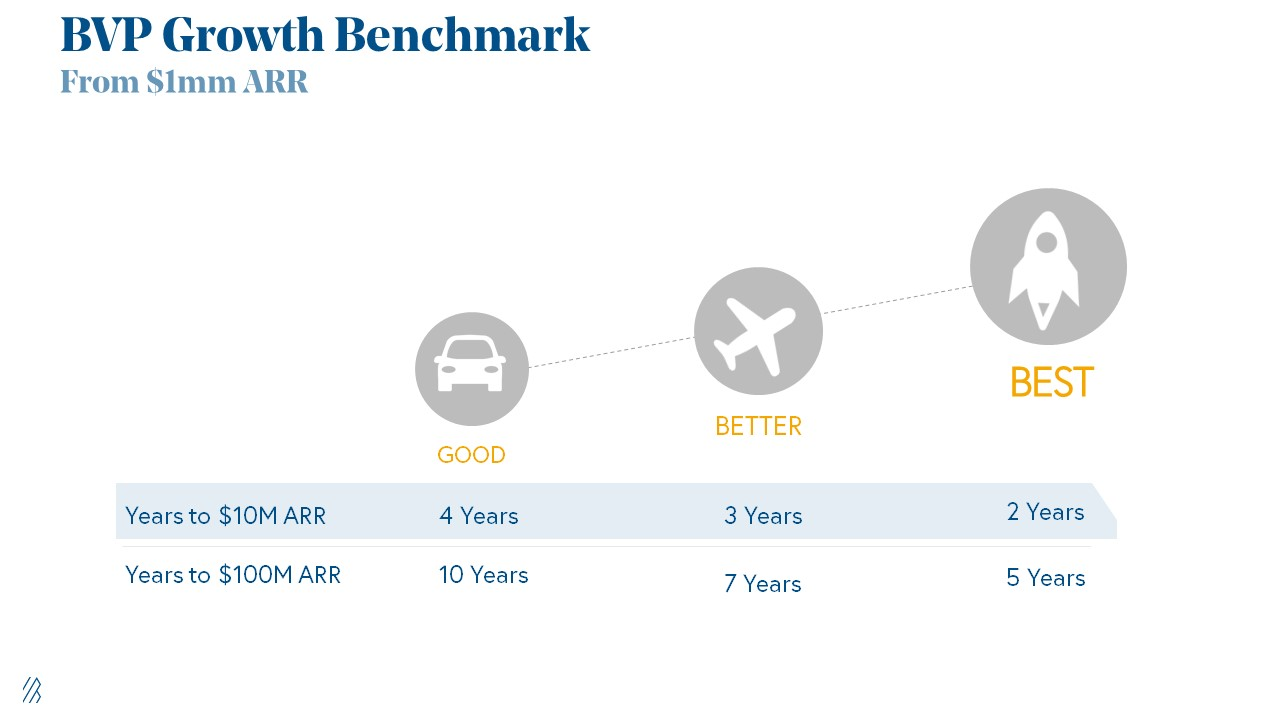
Achieve $1.5m ARR in 12-24 months (Market risk)
Above 100% Net Dollar Retention. (Market danger)
Lead Velocity Rate supporting $10m ARR in 2–4 years (Execution risk)
Hit the 3 and you'll raise $10M in 4 months. Discussing 2/3 may take 6–7 months.
If none, don't bother raising and focus on becoming a capital-efficient business (Topics for other posts).
Let's examine these 3 metrics for the brave ones.
1. Lead Velocity Rate supporting €$10m ARR in 2 to 4 years
Last because it's the least discussed. LVR is the most reliable data when evaluating a growth engine, in my opinion.
SaaS allows you to see the future.
Monthly Sales and Sales Pipelines, two predictive KPIs, have poor data quality. Both are lagging indicators, and minor changes can cause huge modeling differences.
Analysts and Associates will trash your forecasts if they're based only on Monthly Sales and Sales Pipeline.
LVR, defined as month-over-month growth in qualified leads, is rock-solid. There's no lag. You can See The Future if you use Qualified Leads and a consistent formula and process to qualify them.
With this metric in your hand, scaling your company turns into an execution play on which VCs are able to perform calculations risk.
2. Above-100% Net Dollar Retention.
Net Dollar Retention is a better-known SaaS health metric than LVR.
Net Dollar Retention measures a SaaS company's ability to retain and upsell customers. Ask what $1 of net new customer spend will be worth in years n+1, n+2, etc.
Depending on the business model, SaaS businesses can increase their share of customers' wallets by increasing users, selling them more products in SaaS-enabled marketplaces, other add-ons, and renewing them at higher price tiers.
If a SaaS company's annualized Net Dollar Retention is less than 75%, there's a problem with the business.
Slack's ARR chart (below) shows how powerful Net Retention is. Layer chart shows how existing customer revenue grows. Slack's S1 shows 171% Net Dollar Retention for 2017–2019.

Slack S-1
3. $1.5m ARR in the last 12-24 months.
According to Point 9, $0.5m-4m in ARR is needed to raise a $5–12m Series A round.
Target at least what you raised in Pre-Seed/Seed. If you've raised $1.5m since launch, don't raise before $1.5m ARR.
Capital efficiency has returned since Covid19. After raising $2m since inception, it's harder to raise $1m in ARR.

P9's 2016-2021 SaaS Funding Napkin
In summary, less than 1% of companies VCs meet get funded. These metrics can help you win.
If there’s demand for it, I’ll do one on direct-to-consumer.
Cheers!
You might also like

Sammy Abdullah
3 years ago
How to properly price SaaS
Price Intelligently put out amazing content on pricing your SaaS product. This blog's link to the whole report is worth reading. Our key takeaways are below.

Don't base prices on the competition. Competitor-based pricing has clear drawbacks. Their pricing approach is yours. Your company offers customers something unique. Otherwise, you wouldn't create it. This strategy is static, therefore you can't add value by raising prices without outpricing competitors. Look, but don't touch is the competitor-based moral. You want to know your competitors' prices so you're in the same ballpark, but they shouldn't guide your selections. Competitor-based pricing also drives down prices.
Value-based pricing wins. This is customer-based pricing. Value-based pricing looks outward, not inward or laterally at competitors. Your clients are the best source of pricing information. By valuing customer comments, you're focusing on buyers. They'll decide if your pricing and packaging are right. In addition to asking consumers about cost savings or revenue increases, look at data like number of users, usage per user, etc.
Value-based pricing increases prices. As you learn more about the client and your worth, you'll know when and how much to boost rates. Every 6 months, examine pricing.
Cloning top customers. You clone your consumers by learning as much as you can about them and then reaching out to comparable people or organizations. You can't accomplish this without knowing your customers. Segmenting and reproducing them requires as much detail as feasible. Offer pricing plans and feature packages for 4 personas. The top plan should state Contact Us. Your highest-value customers want more advice and support.
Question your 4 personas. What's the one item you can't live without? Which integrations matter most? Do you do analytics? Is support important or does your company self-solve? What's too cheap? What's too expensive?
Not everyone likes per-user pricing. SaaS organizations often default to per-user analytics. About 80% of companies utilizing per-user pricing should use an alternative value metric because their goods don't give more value with more users, so charging for them doesn't make sense.
At least 3:1 LTV/CAC. Break even on the customer within 2 years, and LTV to CAC is greater than 3:1. Because customer acquisition costs are paid upfront but SaaS revenues accrue over time, SaaS companies face an early financial shortfall while paying back the CAC.
ROI should be >20:1. Indeed. Ensure the customer's ROI is 20x the product's cost. Microsoft Office costs $80 a year, but consumers would pay much more to maintain it.
A/B Testing. A/B testing is guessing. When your pricing page varies based on assumptions, you'll upset customers. You don't have enough customers anyway. A/B testing optimizes landing pages, design decisions, and other site features when you know the problem but not pricing.
Don't discount. It cheapens the product, makes it permanent, and increases churn. By discounting, you're ruining your pricing analysis.

Kyle Planck
3 years ago
The chronicles of monkeypox.
or, how I spread monkeypox and got it myself.
This story contains nsfw (not safe for wife) stuff and shouldn't be read if you're under 18 or think I'm a newborn angel. After the opening, it's broken into three sections: a chronological explanation of my disease course, my ideas, and what I plan to do next.
Your journey awaits.
As early as mid-may, I was waltzing around the lab talking about monkeypox, a rare tropical disease with an inaccurate name. Monkeys are not its primary animal reservoir. It caused an outbreak among men who have sex with men across Europe, with unprecedented levels of person-to-person transmission. European health authorities speculated that the virus spread at raves and parties and was easily transferred through intimate, mainly sexual, contact. I had already read the nejm article about the first confirmed monkeypox patient in the u.s. and shared the photos on social media so people knew what to look for. The cdc information page only included 4 photographs of monkeypox lesions that looked like they were captured on a motorola razr.
I warned my ex-boyfriend about monkeypox. Monkeypox? responded.
Mom, I'm afraid about monkeypox. What's monkeypox?
My therapist is scared about monkeypox. What's monkeypox?
Was I alone? A few science gays on Twitter didn't make me feel overreacting.
This information got my gay head turning. The incubation period for the sickness is weeks. Many of my social media contacts are traveling to Europe this summer. What is pride? Travel, parties, and sex. Many people may become infected before attending these activities. Monkeypox will affect the lgbtq+ community.
Being right always stinks. My young scientist brain was right, though. Someone who saw this coming is one of the early victims. I'll talk about my feelings publicly, and trust me, I have many concerning what's occurring.

Part 1 is the specifics.
Wednesday nights are never smart but always entertaining. I didn't wake up until noon on june 23 and saw gay twitter blazing. Without warning, the nyc department of health announced a pop-up monkeypox immunization station in chelsea. Some days would be 11am-7pm. Walk-ins were welcome, however appointments were preferred. I tried to arrange an appointment after rubbing my eyes, but they were all taken. I got out of bed, washed my face, brushed my teeth, and put on short shorts because I wanted to get a walk-in dose and show off my legs. I got a 20-oz. cold brew on the way to the train and texted a chelsea-based acquaintance for help.

Clinic closed at 2pm. No more doses. Hundreds queued up. The government initially gave them only 1,000 dosages. For a city with 500,000 LGBT people, c'mon. What more could I do? I was upset by how things were handled. The evidence speaks for itself.

I decided to seek an appointment when additional doses were available and continued my weekend. I was celebrating nyc pride with pals. Fun! sex! *
On tuesday after that, I felt a little burn. This wasn't surprising because I'd been sexually active throughout the weekend, so I got a sti panel the next day. I expected to get results in a few days, take antibiotics, and move on.
Emerging germs had other intentions. Wednesday night, I felt sore, and thursday morning, I had a blazing temperature and had sweat through my bedding. I had fever, chills, and body-wide aches and pains for three days. I reached 102 degrees. I believed I had covid over pride weekend, but I tested negative for three days straight.
STDs don't induce fevers or other systemic symptoms. If lymphogranuloma venereum advances, it can cause flu-like symptoms and swollen lymph nodes. I was suspicious and desperate for answers, so I researched monkeypox on the cdc website (for healthcare professionals). Much of what I saw on screen about monkeypox prodrome matched my symptoms. Multiple-day fever, headache, muscle aches, chills, tiredness, enlarged lymph nodes. Pox were lacking.
I told my doctor my concerns pre-medically. I'm occasionally annoying.
On saturday night, my fever broke and I felt better. Still burning, I was optimistic till sunday, when I woke up with five red splotches on my arms and fingertips.

As spots formed, burning became pain. I observed as spots developed on my body throughout the day. I had more than a dozen by the end of the day, and the early spots were pustular. I had monkeypox, as feared.

Fourth of July weekend limited my options. I'm well-connected in my school's infectious disease academic community, so I texted a coworker for advice. He agreed it was likely monkeypox and scheduled me for testing on tuesday.
nyc health could only perform 10 monkeypox tests every day. Before doctors could take swabs and send them in, each test had to be approved by the department. Some commercial labs can now perform monkeypox testing, but the backlog is huge. I still don't have a positive orthopoxvirus test five days after my test. *My 12-day-old case may not be included in the official monkeypox tally. This outbreak is far wider than we first thought, therefore I'm attempting to spread the information and help contain it.
*Update, 7/11: I have orthopoxvirus.
I spent all day in the bathtub because of the agony. Warm lavender epsom salts helped me feel better. I can't stand lavender anymore. I brought my laptop into the bathroom and viewed everything everywhere at once (2022). If my ex and I hadn't recently broken up, I wouldn't have monkeypox. All of these things made me cry, and I sat in the bathtub on the 4th of July sobbing. I thought, Is this it? I felt like Bridesmaids' Kristen Wiig (2011). I'm a flop. From here, things can only improve.
Later that night, I wore a mask and went to my roof to see the fireworks. Even though I don't like fireworks, there was something wonderful about them this year: the colors, how they illuminated the black surfaces around me, and their transient beauty. Joyful moments rarely linger long in our life. We must enjoy them now.

Several roofs away, my neighbors gathered. Happy 4th! I heard a woman yell. Why is this godforsaken country so happy? Instead of being rude, I replied. I didn't tell them I had monkeypox. I thought that would kill the mood.
By the time I went to the hospital the next day to get my lesions swabbed, wearing long sleeves, pants, and a mask, they looked like this:
I had 30 lesions on my arms, hands, stomach, back, legs, buttcheeks, face, scalp, and right eyebrow. I had some in my mouth, gums, and throat. Current medical thought is that lesions on mucous membranes cause discomfort in sensitive places. Internal lesions are a new feature of this outbreak of monkeypox. Despite being unattractive, the other sores weren't unpleasant or bothersome.
I had a bacterial sti with the pox. Who knows if that would've created symptoms (often it doesn't), but different infections can happen at once. My care team remembered that having a sti doesn't exclude out monkeypox. doxycycline rocks!
The coworker who introduced me to testing also offered me his home. We share a restroom, and monkeypox can be spread through surfaces. (Being a dna virus gives it environmental hardiness that rna viruses like sars-cov-2 lack.) I disinfected our bathroom after every usage, but I was apprehensive. My friend's place has a guest room and second bathroom, so no cross-contamination. It was the ideal monkeypox isolation environment, so I accepted his offer and am writing this piece there. I don't know what I would have done without his hospitality and attention.
The next day, I started tecovirimat, or tpoxx, for 14 days. Smallpox has been eradicated worldwide since the 1980s but remains a bioterrorism concern. Tecovirimat has a unique, orthopoxvirus-specific method of action, which reduces side effects to headache and nausea. It hasn't been used in many people, therefore the cdc is encouraging patients who take it for monkeypox to track their disease and symptoms.

Tpoxx's oral absorption requires a fatty meal. The hospital ordered me to take the medication after a 600-calorie, 25-gram-fat meal every 12 hours. The coordinator joked, "Don't diet for the next two weeks." I wanted to get peanut butter delivered, but jif is recalling their supply due to salmonella. Please give pathogens a break. I got almond butter.
Tpoxx study enrollment was documented. After signing consent documents, my lesions were photographed and measured during a complete physical exam. I got bloodwork to assess my health. My medication delivery was precise; every step must be accounted for. I got a two-week supply and started taking it that night. I rewarded myself with McDonald's. I'd been hungry for a week. I was also prescribed ketorolac (aka toradol), a stronger ibuprofen, for my discomfort.
I thought tpoxx was a wonder medicine by day two of treatment. Early lesions looked like this.

however, They vanished. The three largest lesions on my back flattened and practically disappeared into my skin. Some pustular lesions were diminishing. Tpoxx+toradol has helped me sleep, focus, and feel human again. I'm down to twice-daily baths and feeling hungrier than ever in this illness. On day five of tpoxx, some of the lesions look like this:

I have a ways to go. We must believe I'll be contagious until the last of my patches scabs over, falls off, and sprouts new skin. There's no way to tell. After a week and a half of tremendous pain and psychological stress, any news is good news. I'm grateful for my slow but steady development.
Part 2 of the rant.
Being close to yet not in the medical world is interesting. It lets me know a lot about it without being persuaded by my involvement. Doctors identify and treat patients using a tool called differential diagnosis.
A doctor interviews a patient to learn about them and their symptoms. More is better. Doctors may ask, "Have you traveled recently?" sex life? Have pets? preferred streaming service? (No, really. (Hbomax is right.) After the inquisition, the doctor will complete a body exam ranging from looking in your eyes, ears, and throat to a thorough physical.
After collecting data, the doctor makes a mental (or physical) inventory of all the conceivable illnesses that could cause or explain the patient's symptoms. Differential diagnosis list. After establishing the differential, the clinician can eliminate options. The doctor will usually conduct nucleic acid tests on swab samples or bloodwork to learn more. This helps eliminate conditions from the differential or boosts a condition's likelihood. In an ideal circumstance, the doctor can eliminate all but one reason of your symptoms, leaving your formal diagnosis. Once diagnosed, treatment can begin. yay! Love medicine.
My symptoms two weeks ago did not suggest monkeypox. Fever, pains, weariness, and swollen lymph nodes are caused by several things. My scandalous symptoms weren't linked to common ones. My instance shows the importance of diversity and representation in healthcare. My doctor isn't gay, but he provides culturally sensitive care. I'd heard about monkeypox as a gay man in New York. I was hyper-aware of it and had heard of friends of friends who had contracted it the week before, even though the official case count in the US was 40. My physicians weren't concerned, but I was. How would it appear on his mental differential if it wasn't on his radar? Mental differential rhymes! I'll trademark it to prevent theft. differential!
I was in a rare position to recognize my condition and advocate for myself. I study infections. I'd spent months researching monkeypox. I work at a university where I rub shoulders with some of the country's greatest doctors. I'm a gay dude who follows nyc queer social networks online. All of these variables positioned me to think, "Maybe this is monkeypox," and to explain why.
This outbreak is another example of privilege at work. The brokenness of our healthcare system is once again exposed by the inequities produced by the vaccination rollout and the existence of people like myself who can pull strings owing to their line of work. I can't cure this situation on my own, but I can be a strong voice demanding the government do a better job addressing the outbreak and giving resources and advice to everyone I can.
lgbtqia+ community members' support has always impressed me in new york. The queer community has watched out for me and supported me in ways I never dreamed were possible.
Queer individuals are there for each other when societal structures fail. People went to the internet on the first day of the vaccine rollout to share appointment information and the vaccine clinic's message. Twitter timelines were more effective than marketing campaigns. Contrary to widespread anti-vaccine sentiment, the LGBT community was eager to protect themselves. Smallpox vaccination? sure. gimme. whether I'm safe. I credit the community's sex positivity. Many people are used to talking about STDs, so there's a reduced barrier to saying, "I think I have something, you should be on the watch too," and taking steps to protect our health.
Once I got monkeypox, I posted on Twitter and Instagram. Besides fueling my main character syndrome, I felt like I wasn't alone. My dc-based friend had monkeypox within hours. He told me about his experience and gave me ideas for managing the discomfort. I can't imagine life without him.
My buddy and colleague organized my medical care and let me remain in his home. His and his husband's friendliness and attention made a world of difference in my recovery. All of my friends and family who helped me, whether by venmo, doordash, or moral support, made me feel cared about. I don't deserve the amazing people in my life.
Finally, I think of everyone who commented on my social media posts regarding my trip. Friends from all sectors of my life and all sexualities have written me well wishes and complimented me for my vulnerability, but I feel the most gravitas from fellow lgbtq+ persons. They're learning to spot. They're learning where to go ill. They're learning self-advocacy. I'm another link in our network of caretaking. I've been cared for, therefore I want to do the same. Community and knowledge are powerful.
You're probably wondering where the diatribe is. You may believe he's gushing about his loved ones, and you'd be right. I say that just because the queer community can take care of itself doesn't mean we should.
Even when caused by the same pathogen, comparing health crises is risky. Aids is unlike covid-19 or monkeypox, yet all were caused by poorly understood viruses. The lgbtq+ community has a history of self-medicating. Queer people (and their supporters) have led the charge to protect themselves throughout history when the government refused. Surreal to experience this in real time.
First, vaccination access is a government failure. The strategic national stockpile contains tens of thousands of doses of jynneos, the newest fda-approved smallpox vaccine, and millions of doses of acam2000, an older vaccine for immunocompetent populations. Despite being a monkeypox hotspot and international crossroads, new york has only received 7,000 doses of the jynneos vaccine. Vaccine appointments are booked within minutes. It's showing Hunger Games, which bothers me.
Second, I think the government failed to recognize the severity of the european monkeypox outbreak. We saw abroad reports in may, but the first vaccines weren't available until june. Why was I a 26-year-old pharmacology grad student, able to see a monkeypox problem in europe but not the u.s. public health agency? Or was there too much bureaucracy and politicking, delaying action?
Lack of testing infrastructure for a known virus with vaccinations and therapies is appalling. More testing would have helped understand the problem's breadth. Many homosexual guys, including myself, didn't behave like monkeypox was a significant threat because there were only a dozen instances across the country. Our underestimating of the issue, spurred by a story of few infections, was huge.
Public health officials' response to infectious diseases frustrates me. A wait-and-see approach to infectious diseases is unsatisfactory. Before a sick person is recognized, they've exposed and maybe contaminated numerous others. Vaccinating susceptible populations before a disease becomes entrenched prevents disease. CDC might operate this way. When it was easier, they didn't control or prevent monkeypox. We'll learn when. Sometimes I fear never. Emerging viral infections are a menace in the era of climate change and globalization, and I fear our government will repeat the same mistakes. I don't work at the cdc, thus I have no idea what they do. As a scientist, a homosexual guy, and a citizen of this country, I feel confident declaring that the cdc has not done enough about monkeypox. Will they do enough about monkeypox? The strategic national stockpile can respond to a bioterrorism disaster in 12 hours. I'm skeptical following this outbreak.
It's simple to criticize the cdc, but they're not to blame. Underfunding public health services, especially the cdc, is another way our government fails to safeguard its citizens. I may gripe about the vaccination rollout all I want, but local health departments are doing their best with limited resources. They may not have enough workers to keep up with demand and run a contact-tracing program. Since my orthopoxvirus test is still negative, the doh hasn't asked about my close contacts. By then, my illness will be two weeks old, too long to do anything productive. Not their fault. They're functioning in a broken system that's underfunded for the work it does.
*Update, 7/11: I have orthopoxvirus.
Monkeypox is slow, so i've had time to contemplate. Now that I'm better, I'm angry. furious and sad I want to help. I wish to spare others my pain. This was preventable and solvable, I hope. HOW?
Third, the duty.
Family, especially selected family, helps each other. So many people have helped me throughout this difficult time. How can I give back? I have ideas.
1. Education. I've already started doing this by writing incredibly detailed posts on Instagram about my physical sickness and my thoughts on the entire scandal. via tweets. by producing this essay. I'll keep doing it even if people start to resent me! It's crucial! On my Instagram profile (@kyleplanckton), you may discover a story highlight with links to all of my bizarre yet educational posts.

2. Resources. I've forwarded the contact information for my institution's infectious diseases clinic to several folks who will hopefully be able to get tpoxx under the expanded use policy. Through my social networks, I've learned of similar institutions. I've also shared crowdsourced resources about symptom relief and vaccine appointment availability on social media. DM me or see my Instagram highlight for more.
3. Community action. During my illness, my friends' willingness to aid me has meant the most. It was nice to know I had folks on my side. One of my pals (thanks, kenny) snagged me a mcgriddle this morning when seamless canceled my order. This scenario has me thinking about methods to help people with monkeypox isolation. A two-week isolation period is financially damaging for many hourly workers. Certain governments required paid sick leave for covid-19 to allow employees to recover and prevent spread. No comparable program exists for monkeypox, and none seems to be planned shortly.
I want to aid monkeypox patients in severe financial conditions. I'm willing to pick up and bring groceries or fund meals/expenses for sick neighbors. I've seen several GoFundMe accounts, but I wish there was a centralized mechanism to link those in need with those who can help. Please contact me if you have expertise with mutual aid organizations. I hope we can start this shortly.
4. lobbying. Personal narratives are powerful. My narrative is only one, but I think it's compelling. Over the next day or so, i'll write to local, state, and federal officials about monkeypox. I wanted a vaccine but couldn't acquire one, and I feel tpoxx helped my disease. As a pharmacologist-in-training, I believe collecting data on a novel medicine is important, and there are ethical problems when making a drug with limited patient data broadly available. Many folks I know can't receive tpoxx due of red tape and a lack of contacts. People shouldn't have to go to an ivy league hospital to obtain the greatest care. Based on my experience and other people's tales, I believe tpoxx can drastically lessen monkeypox patients' pain and potentially curb transmission chains if administered early enough. This outbreak is manageable. It's not too late if we use all the instruments we have (diagnostic, vaccine, treatment).
*UPDATE 7/15: I submitted the following letter to Chuck Schumer and Kirsten Gillibrand. I've addressed identical letters to local, state, and federal officials, including the CDC and HHS.



I hope to join RESPND-MI, an LGBTQ+ community-led assessment of monkeypox symptoms and networks in NYC. Visit their website to learn more and give to this community-based charity.
How I got monkeypox is a mystery. I received it through a pride physical interaction, but i'm not sure which one. This outbreak will expand unless leaders act quickly. Until then, I'll keep educating and connecting people to care in my neighborhood.
Despite my misgivings, I see some optimism. Health department social media efforts are underway. During the outbreak, the CDC provided nonjudgmental suggestions for safer social and sexual activity. There's additional information regarding the disease course online, including how to request tpoxx for sufferers. These materials can help people advocate for themselves if they're sick. Importantly, homosexual guys are listening when they discuss about monkeypox online and irl. Learners They're serious.
The government has a terrible track record with lgtbq+ health issues, and they're not off to a good start this time. I hope this time will be better. If I can aid even one individual, I'll do so.
Thanks for reading, supporting me, and spreading awareness about the 2022 monkeypox outbreak. My dms are accessible if you want info, resources, queries, or to chat.
y'all well
kyle

Michael Hunter, MD
3 years ago
5 Drugs That May Increase Your Risk of Dementia

While our genes can't be changed easily, you can avoid some dementia risk factors. Today we discuss dementia and five drugs that may increase risk.
Memory loss appears to come with age, but we're not talking about forgetfulness. Sometimes losing your car keys isn't an indication of dementia. Dementia impairs the capacity to think, remember, or make judgments. Dementia hinders daily tasks.
Alzheimers is the most common dementia. Dementia is not normal aging, unlike forgetfulness. Aging increases the risk of Alzheimer's and other dementias. A family history of the illness increases your risk, according to the Mayo Clinic (USA).
Given that our genes are difficult to change (I won't get into epigenetics), what are some avoidable dementia risk factors? Certain drugs may cause cognitive deterioration.
Today we look at four drugs that may cause cognitive decline.
Dementia and benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepine sedatives increase brain GABA levels. Example benzodiazepines:
Diazepam (Valium) (Valium)
Alprazolam (Xanax) (Xanax)
Clonazepam (Klonopin) (Klonopin)
Addiction and overdose are benzodiazepine risks. Yes! These medications don't raise dementia risk.
USC study: Benzodiazepines don't increase dementia risk in older adults.
Benzodiazepines can produce short- and long-term amnesia. This memory loss hinders memory formation. Extreme cases can permanently impair learning and memory. Anterograde amnesia is uncommon.
2. Statins and dementia
Statins reduce cholesterol. They prevent a cholesterol-making chemical. Examples:
Atorvastatin (Lipitor) (Lipitor)
Fluvastatin (Lescol XL) (Lescol XL)
Lovastatin (Altoprev) (Altoprev)
Pitavastatin (Livalo, Zypitamag) (Livalo, Zypitamag)
Pravastatin (Pravachol) (Pravachol)
Rosuvastatin (Crestor, Ezallor) (Crestor, Ezallor)
Simvastatin (Zocor) (Zocor)

This finding is contentious. Harvard's Brigham and Womens Hospital's Dr. Joann Manson says:
“I think that the relationship between statins and cognitive function remains controversial. There’s still not a clear conclusion whether they help to prevent dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, have neutral effects, or increase risk.”
This one's off the dementia list.
3. Dementia and anticholinergic drugs
Anticholinergic drugs treat many conditions, including urine incontinence. Drugs inhibit acetylcholine (a brain chemical that helps send messages between cells). Acetylcholine blockers cause drowsiness, disorientation, and memory loss.
First-generation antihistamines, tricyclic antidepressants, and overactive bladder antimuscarinics are common anticholinergics among the elderly.
Anticholinergic drugs may cause dementia. One study found that taking anticholinergics for three years or more increased the risk of dementia by 1.54 times compared to three months or less. After stopping the medicine, the danger may continue.
4. Drugs for Parkinson's disease and dementia
Cleveland Clinic (USA) on Parkinson's:
Parkinson's disease causes age-related brain degeneration. It causes delayed movements, tremors, and balance issues. Some are inherited, but most are unknown. There are various treatment options, but no cure.
Parkinson's medications can cause memory loss, confusion, delusions, and obsessive behaviors. The drug's effects on dopamine cause these issues.
A 2019 JAMA Internal Medicine study found powerful anticholinergic medications enhance dementia risk.
Those who took anticholinergics had a 1.5 times higher chance of dementia. Individuals taking antidepressants, antipsychotic drugs, anti-Parkinson’s drugs, overactive bladder drugs, and anti-epileptic drugs had the greatest risk of dementia.
Anticholinergic medicines can lessen Parkinson's-related tremors, but they slow cognitive ability. Anticholinergics can cause disorientation and hallucinations in those over 70.

5. Antiepileptic drugs and dementia
The risk of dementia from anti-seizure drugs varies with drugs. Levetiracetam (Keppra) improves Alzheimer's cognition.
One study linked different anti-seizure medications to dementia. Anti-epileptic medicines increased the risk of Alzheimer's disease by 1.15 times in the Finnish sample and 1.3 times in the German population. Depakote, Topamax are drugs.
