More on Entrepreneurship/Creators

Victoria Kurichenko
3 years ago
Here's what happened after I launched my second product on Gumroad.
One-hour ebook sales, affiliate relationships, and more.

If you follow me, you may know I started a new ebook in August 2022.
Despite publishing on this platform, my website, and Quora, I'm not a writer.
My writing speed is slow, 2,000 words a day, and I struggle to communicate cohesively.
In April 2022, I wrote a successful guide on How to Write Google-Friendly Blog Posts.
I had no email list or social media presence. I've made $1,600+ selling ebooks.
Evidence:

My first digital offering isn't a book.
It's an actionable guide with my tried-and-true process for writing Google-friendly content.
I'm not bragging.
Established authors like Tim Denning make more from my ebook sales with one newsletter.
This experience taught me writing isn't a privilege.
Writing a book and making money online doesn't require expertise.
Many don't consult experts. They want someone approachable.
Two years passed before I realized my own limits.
I have a brain, two hands, and Internet to spread my message.
I wrote and published a second ebook after the first's success.
On Gumroad, I released my second digital product.
Here's my complete Gumroad evaluation.
Gumroad is a marketplace for content providers to develop and sell sales pages.
Gumroad handles payments and client requests. It's helpful when someone sends a bogus payment receipt requesting an ebook (actual story!).
You'll forget administrative concerns after your first ebook sale.
After my first ebook sale, I did this: I made additional cash!
After every sale, I tell myself, "I built a new semi-passive revenue source."
This thinking shift helps me become less busy while increasing my income and quality of life.
Besides helping others, folks sell evergreen digital things to earn passive money.
It's in my second ebook.
I explain how I built and sold 50+ copies of my SEO writing ebook without being an influencer.
I show how anyone can sell ebooks on Gumroad and automate their sales process.
This is my ebook.

After publicizing the ebook release, I sold three copies within an hour.
Wow, or meh?
I don’t know.
The answer is different for everyone.
These three sales came from a small email list of 40 motivated fans waiting for my ebook release.
I had bigger plans.
I'll market my ebook on Medium, my website, Quora, and email.
I'm testing affiliate partnerships this time.
One of my ebook buyers is now promoting it for 40% commission.
Become my affiliate if you think your readers would like my ebook.
My ebook is a few days old, but I'm interested to see where it goes.
My SEO writing book started without an email list, affiliates, or 4,000 website visitors. I've made four figures.
I'm slowly expanding my communication avenues to have more impact.
Even a small project can open doors you never knew existed.
So began my writing career.
In summary
If you dare, every concept can become a profitable trip.
Before, I couldn't conceive of creating an ebook.
How to Sell eBooks on Gumroad is my second digital product.
Marketing and writing taught me that anything can be sold online.

Jenn Leach
3 years ago
In November, I made an effort to pitch 10 brands per day. Here's what I discovered.

I pitched 10 brands per workday for a total of 200.
How did I do?
It was difficult.
I've never pitched so much.
What did this challenge teach me?
the superiority of quality over quantity
When you need help, outsource
Don't disregard burnout in order to complete a challenge because it exists.
First, pitching brands for brand deals requires quality. Find firms that align with your brand to expose to your audience.
If you associate with any company, you'll lose audience loyalty. I didn't lose sight of that, but I couldn't resist finishing the task.
Outsourcing.
Delegating work to teammates is effective.
I wish I'd done it.
Three people can pitch 200 companies a month significantly faster than one.
One person does research, one to two do outreach, and one to two do follow-up and negotiating.
Simple.
In 2022, I'll outsource everything.
Burnout.
I felt this, so I slowed down at the end of the month.
Thanksgiving week in November was slow.
I was buying and decorating for Christmas. First time putting up outdoor holiday lights was fun.
Much was happening.
I'm not perfect.
I'm being honest.
The Outcomes
Less than 50 brands pitched.
Result: A deal with 3 brands.
I hoped for 4 brands with reaching out to 200 companies, so three with under 50 is wonderful.
That’s a 6% conversion rate!
Whoo-hoo!
I needed 2%.
Here's a screenshot from one of the deals I booked.

These companies fit my company well. Each campaign is different, but I've booked $2,450 in brand work with a couple of pending transactions for December and January.
$2,450 in brand work booked!
How did I do? You tell me.
Is this something you’d try yourself?

Owolabi Judah
3 years ago
How much did YouTube pay for 10 million views?
Ali's $1,054,053.74 YouTube Adsense haul.

YouTuber, entrepreneur, and former doctor Ali Abdaal. He began filming productivity and financial videos in 2017. Ali Abdaal has 3 million YouTube subscribers and has crossed $1 million in AdSense revenue. Crazy, no?
Ali will share the revenue of his top 5 youtube videos, things he's learned that you can apply to your side hustle, and how many views it takes to make a livelihood off youtube.
First, "The Long Game."
All good things take time to bear fruit. Compounding improves everything. Long-term work yields better returns. Ali made his first dollar after nine months and 85 videos.

Second, "One piece of content can transform your life, but you never know which one."

Had he abandoned YouTube at 84 videos without making any money, he wouldn't have filmed the 85th video that altered everything.
Third Lesson: Your Industry Choice Can Multiply.
The industry or niche you target as a business owner or side hustler can have a major impact on how much money you make.
Here are the top 5 videos.

1) 9.8m views: $191,258.16 for 9 passive income ideas

Ali made 2 points.
We should consider YouTube videos digital assets. They're investments, which make us money. His investments are yielding passive income.
Investing extra time and effort in your films can pay off.
2) How to Invest for Beginners — 5.2m Views: $87,200.08.

This video did poorly in the first several weeks after it was published; it was his tenth poorest performer. Don't worry about things you can't control. This applies to life, not just YouTube videos.
He stated we constantly have anxieties, fears, and concerns about things outside our control, but if we can find that line, life is easier and more pleasurable.
3) How to Build a Website in 2022— 866.3k views: $42,132.72.

The RPM was $48.86 per thousand views, making it his highest-earning video. Squarespace, Wix, and other website builders are trying to put ads on it and competing against one other, so ad rates go up.
Because it was beyond his niche, Ali almost didn't make the video. He made the video because he wanted to help at least one person.
4) How I take notes on my iPad in medical school — 5.9m views: $24,479.80

85th video. It's the video that affected Ali's YouTube channel and his life the most. The video's success wasn't certain.
5) How I Type Fast 156 Words Per Minute — 8.2M views: $25,143.17

Ali didn't know this video would perform well; he made it because he can type fast and has been practicing for 10 years. So he made a video with his best advice.
How many views to different wealth levels?
It depends on geography, niche, and other monetization sources. To keep things simple, he would solely utilize AdSense.
How many views to generate money?

To generate money on Youtube, you need 1,000 subscribers and 4,000 hours of view time. How much work do you need to make pocket money?

Ali's first 1,000 subscribers took 52 videos and 6 months. The typical channel with 1,000 subscribers contains 152 videos, according to Tubebuddy. It's time-consuming.
After monetizing, you'll need 15,000 views/month to make $5-$10/day.
How many views to go part-time?

Say you make $35,000/year at your day job. If you work 5 days/week, you make $7,000/year each day. If you want to drop down from 5 days to 4 days/week, you need to make an extra $7,000/year from YouTube, or $600/month.
What's the quit-your-job budget?

Silicon Valley Girl is in a highly successful niche targeting tech-focused folks in the west. When her channel had 500k views/month, she made roughly $3,000/month or $47,000/year, enough to quit your work.
Marina has another 1.5m subscriber channel in Russia, which has a lower rpm because fewer corporations advertise there than in the west. 2.3 million views/month is $4,000/month or $50,000/year, enough to quit your employment.

Marina is an intriguing example because she has three YouTube channels with the same skills, but one is 16x more profitable due to the niche she chose.
In Ali's case, he made 100+ videos when his channel was producing enough money to quit his job, roughly $4,000/month.
How many views make you rich?

Depending on how you define rich. Ali felt prosperous with over $100,000/year and 3–5m views/month.
Conclusion
YouTubers and artists don't treat their work like a company, which is a mistake. Businesses have been attempting to figure this out for decades, if not centuries.
We can learn from the business world how to monetize YouTube, Instagram, and Tiktok and make them into sustainable enterprises where we can hire people and delegate tasks.
Bonus
Watch Ali's video explaining all this:
This post is a summary. Read the full article here
You might also like

Arthur Hayes
3 years ago
Contagion
(The author's opinions should not be used to make investment decisions or as a recommendation to invest.)

The pandemic and social media pseudoscience have made us all epidemiologists, for better or worse. Flattening the curve, social distancing, lockdowns—remember? Some of you may remember R0 (R naught), the number of healthy humans the average COVID-infected person infects. Thankfully, the world has moved on from Greater China's nightmare. Politicians have refocused their talent for misdirection on getting their constituents invested in the war for Russian Reunification or Russian Aggression, depending on your side of the iron curtain.
Humanity battles two fronts. A war against an invisible virus (I know your Commander in Chief might have told you COVID is over, but viruses don't follow election cycles and their economic impacts linger long after the last rapid-test clinic has closed); and an undeclared World War between US/NATO and Eurasia/Russia/China. The fiscal and monetary authorities' current policies aim to mitigate these two conflicts' economic effects.
Since all politicians are short-sighted, they usually print money to solve most problems. Printing money is the easiest and fastest way to solve most problems because it can be done immediately without much discussion. The alternative—long-term restructuring of our global economy—would hurt stakeholders and require an honest discussion about our civilization's state. Both of those requirements are non-starters for our short-sighted political friends, so whether your government practices capitalism, communism, socialism, or fascism, they all turn to printing money-ism to solve all problems.
Free money stimulates demand, so people buy crap. Overbuying shit raises prices. Inflation. Every nation has food, energy, or goods inflation. The once-docile plebes demand action when the latter two subsets of inflation rise rapidly. They will be heard at the polls or in the streets. What would you do to feed your crying hungry child?
Global central banks During the pandemic, the Fed, PBOC, BOJ, ECB, and BOE printed money to aid their governments. They worried about inflation and promised to remove fiat liquidity and tighten monetary conditions.
Imagine Nate Diaz's round-house kick to the face. The financial markets probably felt that way when the US and a few others withdrew fiat wampum. Sovereign debt markets suffered a near-record bond market rout.
The undeclared WW3 is intensifying, with recent gas pipeline attacks. The global economy is already struggling, and credit withdrawal will worsen the situation. The next pandemic, the Yield Curve Control (YCC) virus, is spreading as major central banks backtrack on inflation promises. All central banks eventually fail.
Here's a scorecard.
In order to save its financial system, BOE recently reverted to Quantitative Easing (QE).
BOJ Continuing YCC to save their banking system and enable affordable government borrowing.
ECB printing money to buy weak EU member bonds, but will soon start Quantitative Tightening (QT).
PBOC Restarting the money printer to give banks liquidity to support the falling residential property market.
Fed raising rates and QT-shrinking balance sheet.
80% of the world's biggest central banks are printing money again. Only the Fed has remained steadfast in the face of a financial market bloodbath, determined to end the inflation for which it is at least partially responsible—the culmination of decades of bad economic policies and a world war.
YCC printing is the worst for fiat currency and society. Because it necessitates central banks fixing a multi-trillion-dollar bond market. YCC central banks promise to infinitely expand their balance sheets to keep a certain interest rate metric below an unnatural ceiling. The market always wins, crushing humanity with inflation.
BOJ's YCC policy is longest-standing. The BOE joined them, and my essay this week argues that the ECB will follow. The ECB joining YCC would make 60% of major central banks follow this terrible policy. Since the PBOC is part of the Chinese financial system, the number could be 80%. The Chinese will lend any amount to meet their economic activity goals.
The BOE committed to a 13-week, GBP 65bn bond price-fixing operation. However, BOEs YCC may return. If you lose to the market, you're stuck. Since the BOE has announced that it will buy your Gilt at inflated prices, why would you not sell them all? Market participants taking advantage of this policy will only push the bank further into the hole it dug itself, so I expect the BOE to re-up this program and count them as YCC.
In a few trading days, the BOE went from a bank determined to slay inflation by raising interest rates and QT to buying an unlimited amount of UK Gilts. I expect the ECB to be dragged kicking and screaming into a similar policy. Spoiler alert: big daddy Fed will eventually die from the YCC virus.
Threadneedle St, London EC2R 8AH, UK
Before we discuss the BOE's recent missteps, a chatroom member called the British royal family the Kardashians with Crowns, which made me laugh. I'm sad about royal attention. If the public was as interested in energy and economic policies as they are in how the late Queen treated Meghan, Duchess of Sussex, UK politicians might not have been able to get away with energy and economic fairy tales.
The BOE printed money to recover from COVID, as all good central banks do. For historical context, this chart shows the BOE's total assets as a percentage of GDP since its founding in the 18th century.

The UK has had a rough three centuries. Pandemics, empire wars, civil wars, world wars. Even so, the BOE's recent money printing was its most aggressive ever!
BOE Total Assets as % of GDP (white) vs. UK CPI

Now, inflation responded slowly to the bank's most aggressive monetary loosening. King Charles wishes the gold line above showed his popularity, but it shows his subjects' suffering.
The BOE recognized early that its money printing caused runaway inflation. In its August 2022 report, the bank predicted that inflation would reach 13% by year end before aggressively tapering in 2023 and 2024.

Aug 2022 BOE Monetary Policy Report
The BOE was the first major central bank to reduce its balance sheet and raise its policy rate to help.

The BOE first raised rates in December 2021. Back then, JayPow wasn't even considering raising rates.
UK policymakers, like most developed nations, believe in energy fairy tales. Namely, that the developed world, which grew in lockstep with hydrocarbon use, could switch to wind and solar by 2050. The UK's energy import bill has grown while coal, North Sea oil, and possibly stranded shale oil have been ignored.

WW3 is an economic war that is balkanizing energy markets, which will continue to inflate. A nation that imports energy and has printed the most money in its history cannot avoid inflation.

The chart above shows that energy inflation is a major cause of plebe pain.
The UK is hit by a double whammy: the BOE must remove credit to reduce demand, and energy prices must rise due to WW3 inflation. That's not economic growth.
Boris Johnson was knocked out by his country's poor economic performance, not his lockdown at 10 Downing St. Prime Minister Truss and her merry band of fools arrived with the tried-and-true government remedy: goodies for everyone.
She released a budget full of economic stimulants. She cut corporate and individual taxes for the rich. She plans to give poor people vouchers for higher energy bills. Woohoo! Margret Thatcher's new pants suit.
My buddy Jim Bianco said Truss budget's problem is that it works. It will boost activity at a time when inflation is over 10%. Truss' budget didn't include austerity measures like tax increases or spending cuts, which the bond market wanted. The bond market protested.

30-year Gilt yield chart. Yields spiked the most ever after Truss announced her budget, as shown. The Gilt market is the longest-running bond market in the world.

The Gilt market showed the pole who's boss with Cardi B.
Before this, the BOE was super-committed to fighting inflation. To their credit, they raised short-term rates and shrank their balance sheet. However, rapid yield rises threatened to destroy the entire highly leveraged UK financial system overnight, forcing them to change course.
Accounting gimmicks allowed by regulators for pension funds posed a systemic threat to the UK banking system. UK pension funds could use interest rate market levered derivatives to match liabilities. When rates rise, short rate derivatives require more margin. The pension funds spent all their money trying to pick stonks and whatever else their sell side banker could stuff them with, so the historic rate spike would have bankrupted them overnight. The FT describes BOE-supervised chicanery well.
To avoid a financial apocalypse, the BOE in one morning abandoned all their hard work and started buying unlimited long-dated Gilts to drive prices down.

Another reminder to never fight a central bank. The 30-year Gilt is shown above. After the BOE restarted the money printer on September 28, this bond rose 30%. Thirty-fucking-percent! Developed market sovereign bonds rarely move daily. You're invested in His Majesty's government obligations, not a Chinese property developer's offshore USD bond.
The political need to give people goodies to help them fight the terrible economy ran into a financial reality. The central bank protected the UK financial system from asset-price deflation because, like all modern economies, it is debt-based and highly levered. As bad as it is, inflation is not their top priority. The BOE example demonstrated that. To save the financial system, they abandoned almost a year of prudent monetary policy in a few hours. They also started the endgame.
Let's play Central Bankers Say the Darndest Things before we go to the continent (and sorry if you live on a continent other than Europe, but you're not culturally relevant).
Pre-meltdown BOE output:
FT, October 17, 2021 On Sunday, the Bank of England governor warned that it must act to curb inflationary pressure, ignoring financial market moves that have priced in the first interest rate increase before the end of the year.
On July 19, 2022, Gov. Andrew Bailey spoke. Our 2% inflation target is unwavering. We'll do our job.
August 4th 2022 MPC monetary policy announcement According to its mandate, the MPC will sustainably return inflation to 2% in the medium term.
Catherine Mann, MPC member, September 5, 2022 speech. Fast and forceful monetary tightening, possibly followed by a hold or reversal, is better than gradualism because it promotes inflation expectations' role in bringing inflation back to 2% over the medium term.
When their financial system nearly collapsed in one trading session, they said:
The Bank of England's Financial Policy Committee warned on 28 September that gilt market dysfunction threatened UK financial stability. It advised action and supported the Bank's urgent gilt market purchases for financial stability.
It works when the price goes up but not down. Is my crypto portfolio dysfunctional enough to get a BOE bailout?
Next, the EU and ECB. The ECB is also fighting inflation, but it will also succumb to the YCC virus for the same reasons as the BOE.
Frankfurt am Main, ECB Tower, Sonnemannstraße 20, 60314
Only France and Germany matter economically in the EU. Modern European history has focused on keeping Germany and Russia apart. German manufacturing and cheap Russian goods could change geopolitics.
France created the EU to keep Germany down, and the Germans only cooperated because of WWII guilt. France's interests are shared by the US, which lurks in the shadows to prevent a Germany-Russia alliance. A weak EU benefits US politics. Avoid unification of Eurasia. (I paraphrased daddy Felix because I thought quoting a large part of his most recent missive would get me spanked.)
As with everything, understanding Germany's energy policy is the best way to understand why the German economy is fundamentally fucked and why that spells doom for the EU. Germany, the EU's main economic engine, is being crippled by high energy prices, threatening a depression. This economic downturn threatens the union. The ECB may have to abandon plans to shrink its balance sheet and switch to YCC to save the EU's unholy political union.
France did the smart thing and went all in on nuclear energy, which is rare in geopolitics. 70% of electricity is nuclear-powered. Their manufacturing base can survive Russian gas cuts. Germany cannot.
My boy Zoltan made this great graphic showing how screwed Germany is as cheap Russian gas leaves the industrial economy.

$27 billion of Russian gas powers almost $2 trillion of German economic output, a 75x energy leverage. The German public was duped into believing the same energy fairy tales as their politicians, and they overwhelmingly allowed the Green party to dismantle any efforts to build a nuclear energy ecosystem over the past several decades. Germany, unlike France, must import expensive American and Qatari LNG via supertankers due to Nordstream I and II pipeline sabotage.
American gas exports to Europe are touted by the media. Gas is cheap because America isn't the Western world's swing producer. If gas prices rise domestically in America, the plebes would demand the end of imports to avoid paying more to heat their homes.
German goods would cost much more in this scenario. German producer prices rose 46% YoY in August. The German current account is rapidly approaching zero and will soon be negative.
German PPI Change YoY

German Current Account

The reason this matters is a curious construction called TARGET2. Let’s hear from the horse’s mouth what exactly this beat is:
TARGET2 is the real-time gross settlement (RTGS) system owned and operated by the Eurosystem. Central banks and commercial banks can submit payment orders in euro to TARGET2, where they are processed and settled in central bank money, i.e. money held in an account with a central bank.
Source: ECB
Let me explain this in plain English for those unfamiliar with economic dogma.

This chart shows intra-EU credits and debits. TARGET2. Germany, Europe's powerhouse, is owed money. IOU-buying Greeks buy G-wagons. The G-wagon pickup truck is badass.

If all EU countries had fiat currencies, the Deutsche Mark would be stronger than the Italian Lira, according to the chart above. If Europe had to buy goods from non-EU countries, the Euro would be much weaker. Credits and debits between smaller political units smooth out imbalances in other federal-provincial-state political systems. Financial and fiscal unions allow this. The EU is financial, so the centre cannot force the periphery to settle their imbalances.
Greece has never had to buy Fords or Kias instead of BMWs, but what if Germany had to shut down its auto manufacturing plants due to energy shortages?
Italians have done well buying ammonia from Germany rather than China, but what if BASF had to close its Ludwigshafen facility due to a lack of affordable natural gas?
I think you're seeing the issue.
Instead of Germany, EU countries would owe foreign producers like America, China, South Korea, Japan, etc. Since these countries aren't tied into an uneconomic union for politics, they'll demand hard fiat currency like USD instead of Euros, which have become toilet paper (or toilet plastic).
Keynesian economists have a simple solution for politicians who can't afford market prices. Government debt can maintain production. The debt covers the difference between what a business can afford and the international energy market price.
Germans are monetary policy conservative because of the Weimar Republic's hyperinflation. The Bundesbank is the only thing preventing ECB profligacy. Germany must print its way out without cheap energy. Like other nations, they will issue more bonds for fiscal transfers.
More Bunds mean lower prices. Without German monetary discipline, the Euro would have become a trash currency like any other emerging market that imports energy and food and has uncompetitive labor.
Bunds price all EU country bonds. The ECB's money printing is designed to keep the spread of weak EU member bonds vs. Bunds low. Everyone falls with Bunds.
Like the UK, German politicians seeking re-election will likely cause a Bunds selloff. Bond investors will understandably reject their promises of goodies for industry and individuals to offset the lack of cheap Russian gas. Long-dated Bunds will be smoked like UK Gilts. The ECB will face a wave of ultra-levered financial players who will go bankrupt if they mark to market their fixed income derivatives books at higher Bund yields.
Some treats People: Germany will spend 200B to help consumers and businesses cope with energy prices, including promoting renewable energy.
That, ladies and germs, is why the ECB will immediately abandon QT, move to a stop-gap QE program to normalize the Bund and every other EU bond market, and eventually graduate to YCC as the market vomits bonds of all stripes into Christine Lagarde's loving hands. She probably has soft hands.
The 30-year Bund market has noticed Germany's economic collapse. 2021 yields skyrocketed.
30-year Bund Yield

ECB Says the Darndest Things:
Because inflation is too high and likely to stay above our target for a long time, we took today's decision and expect to raise interest rates further.- Christine Lagarde, ECB Press Conference, Sept 8.
The Governing Council will adjust all of its instruments to stabilize inflation at 2% over the medium term. July 21 ECB Monetary Decision
Everyone struggles with high inflation. The Governing Council will ensure medium-term inflation returns to two percent. June 9th ECB Press Conference
I'm excited to read the after. Like the BOE, the ECB may abandon their plans to shrink their balance sheet and resume QE due to debt market dysfunction.
Eighty Percent
I like YCC like dark chocolate over 80%. ;).
Can 80% of the world's major central banks' QE and/or YCC overcome Sir Powell's toughness on fungible risky asset prices?
Gold and crypto are fungible global risky assets. Satoshis and gold bars are the same in New York, London, Frankfurt, Tokyo, and Shanghai.
As more Euros, Yen, Renminbi, and Pounds are printed, people will move their savings into Dollars or other stores of value. As the Fed raises rates and reduces its balance sheet, the USD will strengthen. Gold/EUR and BTC/JPY may also attract buyers.
Gold and crypto markets are much smaller than the trillions in fiat money that will be printed, so they will appreciate in non-USD currencies. These flows only matter in one instance because we trade the global or USD price. Arbitrage occurs when BTC/EUR rises faster than EUR/USD. Here is how it works:
An investor based in the USD notices that BTC is expensive in EUR terms.
Instead of buying BTC, this investor borrows USD and then sells it.
After that, they sell BTC and buy EUR.
Then they choose to sell EUR and buy USD.
The investor receives their profit after repaying the USD loan.
This triangular FX arbitrage will align the global/USD BTC price with the elevated EUR, JPY, CNY, and GBP prices.
Even if the Fed continues QT, which I doubt they can do past early 2023, small stores of value like gold and Bitcoin may rise as non-Fed central banks get serious about printing money.
“Arthur, this is just more copium,” you might retort.
Patience. This takes time. Economic and political forcing functions take time. The BOE example shows that bond markets will reject politicians' policies to appease voters. Decades of bad energy policy have no immediate fix. Money printing is the only politically viable option. Bond yields will rise as bond markets see more stimulative budgets, and the over-leveraged fiat debt-based financial system will collapse quickly, followed by a monetary bailout.
America has enough food, fuel, and people. China, Europe, Japan, and the UK suffer. America can be autonomous. Thus, the Fed can prioritize domestic political inflation concerns over supplying the world (and most of its allies) with dollars. A steady flow of dollars allows other nations to print their currencies and buy energy in USD. If the strongest player wins, everyone else loses.
I'm making a GDP-weighted index of these five central banks' money printing. When ready, I'll share its rate of change. This will show when the 80%'s money printing exceeds the Fed's tightening.
Matthew Royse
3 years ago
7 ways to improve public speaking
How to overcome public speaking fear and give a killer presentation

"Public speaking is people's biggest fear, according to studies. Death's second. The average person is better off in the casket than delivering the eulogy." — American comedian, actor, writer, and producer Jerry Seinfeld
People fear public speaking, according to research. Public speaking can be intimidating.
Most professions require public speaking, whether to 5, 50, 500, or 5,000 people. Your career will require many presentations. In a small meeting, company update, or industry conference.
You can improve your public speaking skills. You can reduce your anxiety, improve your performance, and feel more comfortable speaking in public.
“If I returned to college, I'd focus on writing and public speaking. Effective communication is everything.” — 38th president Gerald R. Ford
You can deliver a great presentation despite your fear of public speaking. There are ways to stay calm while speaking and become a more effective public speaker.
Seven tips to improve your public speaking today. Let's help you overcome your fear (no pun intended).
Know your audience.
"You're not being judged; the audience is." — Entrepreneur, author, and speaker Seth Godin
Understand your audience before speaking publicly. Before preparing a presentation, know your audience. Learn what they care about and find useful.
Your presentation may depend on where you're speaking. A classroom is different from a company meeting.
Determine your audience before developing your main messages. Learn everything about them. Knowing your audience helps you choose the right words, information (thought leadership vs. technical), and motivational message.
2. Be Observant
Observe others' speeches to improve your own. Watching free TED Talks on education, business, science, technology, and creativity can teach you a lot about public speaking.
What worked and what didn't?
What would you change?
Their strengths
How interesting or dull was the topic?
Note their techniques to learn more. Studying the best public speakers will amaze you.
Learn how their stage presence helped them communicate and captivated their audience. Please note their pauses, humor, and pacing.
3. Practice
"A speaker should prepare based on what he wants to learn, not say." — Author, speaker, and pastor Tod Stocker
Practice makes perfect when it comes to public speaking. By repeating your presentation, you can find your comfort zone.
When you've practiced your presentation many times, you'll feel natural and confident giving it. Preparation helps overcome fear and anxiety. Review notes and important messages.
When you know the material well, you can explain it better. Your presentation preparation starts before you go on stage.
Keep a notebook or journal of ideas, quotes, and examples. More content means better audience-targeting.
4. Self-record
Videotape your speeches. Check yourself. Body language, hands, pacing, and vocabulary should be reviewed.
Best public speakers evaluate their performance to improve.
Write down what you did best, what you could improve and what you should stop doing after watching a recording of yourself. Seeing yourself can be unsettling. This is how you improve.
5. Remove text from slides
"Humans can't read and comprehend screen text while listening to a speaker. Therefore, lots of text and long, complete sentences are bad, bad, bad.” —Communications expert Garr Reynolds
Presentation slides shouldn't have too much text. 100-slide presentations bore the audience. Your slides should preview what you'll say to the audience.
Use slides to emphasize your main point visually.
If you add text, use at least 40-point font. Your slides shouldn't require squinting to read. You want people to watch you, not your slides.
6. Body language
"Body language is powerful." We had body language before speech, and 80% of a conversation is read through the body, not the words." — Dancer, writer, and broadcaster Deborah Bull
Nonverbal communication dominates. Our bodies speak louder than words. Don't fidget, rock, lean, or pace.
Relax your body to communicate clearly and without distraction through nonverbal cues. Public speaking anxiety can cause tense body language.
Maintain posture and eye contact. Don’t put your hand in your pockets, cross your arms, or stare at your notes. Make purposeful hand gestures that match what you're saying.
7. Beginning/ending Strong
Beginning and end are memorable. Your presentation must start strong and end strongly. To engage your audience, don't sound robotic.
Begin with a story, stat, or quote. Conclude with a summary of key points. Focus on how you will start and end your speech.
You should memorize your presentation's opening and closing. Memorize something naturally. Excellent presentations start and end strong because people won't remember the middle.
Bringing It All Together
Seven simple yet powerful ways to improve public speaking. Know your audience, study others, prepare and rehearse, record yourself, remove as much text as possible from slides, and start and end strong.
Follow these tips to improve your speaking and audience communication. Prepare, practice, and learn from great speakers to reduce your fear of public speaking.
"Speaking to one person or a thousand is public speaking." — Vocal coach Roger Love

Joseph Mavericks
3 years ago
The world's 36th richest man uses a 5-step system to get what he wants.
Ray Dalio's super-effective roadmap

Ray Dalio's $22 billion net worth ranks him 36th globally. From 1975 to 2011, he built the world's most successful hedge fund, never losing more than 4% from 1991 to 2020. (and only doing so during 3 calendar years).
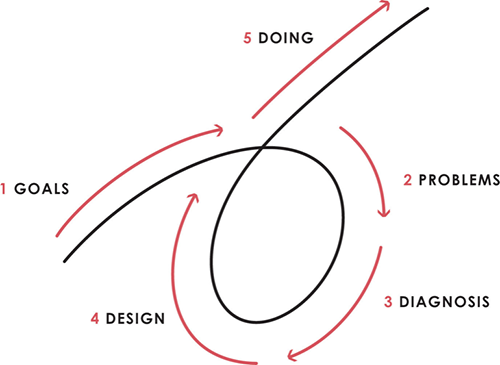
Dalio describes a 5-step process in his best-selling book Principles. It's the playbook he's used to build his hedge fund, beat the markets, and face personal challenges.
This 5-step system is so valuable and well-explained that I didn't edit or change anything; I only added my own insights in the parts I found most relevant and/or relatable as a young entrepreneur. The system's overview:
Have clear goals
Identify and don’t tolerate problems
Diagnose problems to get at their root causes
Design plans that will get you around those problems
Do what is necessary to push through the plans to get results
If you follow these 5 steps in a virtuous loop, you'll almost always see results. Repeat the process for each goal you have.
1. Have clear goals
a) Prioritize: You can have almost anything, but not everything.
I started and never launched dozens of projects for 10 years because I was scattered. I opened a t-shirt store, traded algorithms, sold art on Instagram, painted skateboards, and tinkered with electronics. I decided to try blogging for 6 months to see where it took me. Still going after 3 years.
b) Don’t confuse goals with desires.
A goal inspires you to act. Unreasonable desires prevent you from achieving your goals.
c) Reconcile your goals and desires to decide what you want.
d) Don't confuse success with its trappings.
e) Never dismiss a goal as unattainable.
Always one path is best. Your perception of what's possible depends on what you know now. I never thought I'd make money writing online so quickly, and now I see a whole new horizon of business opportunities I didn't know about before.
f) Expectations create abilities.
Don't limit your abilities. More you strive, the more you'll achieve.
g) Flexibility and self-accountability can almost guarantee success.
Flexible people accept what reality or others teach them. Self-accountability is the ability to recognize your mistakes and be more creative, flexible, and determined.
h) Handling setbacks well is as important as moving forward.
Learn when to minimize losses and when to let go and move on.
2. Don't ignore problems
a) See painful problems as improvement opportunities.
Every problem, painful situation, and challenge is an opportunity. Read The Art of Happiness for more.
b) Don't avoid problems because of harsh realities.
Recognizing your weaknesses isn't the same as giving in. It's the first step in overcoming them.
c) Specify your issues.
There is no "one-size-fits-all" solution.
d) Don’t mistake a cause of a problem with the real problem.
"I can't sleep" is a cause, not a problem. "I'm underperforming" could be a problem.
e) Separate big from small problems.
You have limited time and energy, so focus on the biggest problems.
f) Don't ignore a problem.
Identifying a problem and tolerating it is like not identifying it.
3. Identify problems' root causes
a) Decide "what to do" after assessing "what is."
"A good diagnosis takes 15 to 60 minutes, depending on its accuracy and complexity. [...] Like principles, root causes recur in different situations.
b) Separate proximate and root causes.
"You can only solve problems by removing their root causes, and to do that, you must distinguish symptoms from disease."
c) Knowing someone's (or your own) personality can help you predict their behavior.
4. Design plans that will get you around the problems
a) Retrace your steps.
Analyze your past to determine your future.
b) Consider your problem a machine's output.
Consider how to improve your machine. It's a game then.
c) There are many ways to reach your goals.
Find a solution.
d) Visualize who will do what in your plan like a movie script.
Consider your movie's actors and script's turning points, then act accordingly. The game continues.
e) Document your plan so others can judge your progress.
Accountability boosts success.
f) Know that a good plan doesn't take much time.
The execution is usually the hardest part, but most people either don't have a plan or keep changing it. Don't drive while building the car. Build it first, because it'll be bumpy.
5. Do what is necessary to push through the plans to get results
a) Great planners without execution fail.
Life is won with more than just planning. Similarly, practice without talent beats talent without practice.
b) Work ethic is undervalued.
Hyper-productivity is praised in corporate America, even if it leads nowhere. To get things done, use checklists, fewer emails, and more desk time.
c) Set clear metrics to ensure plan adherence.
I've written about the OKR strategy for organizations with multiple people here. If you're on your own, I recommend the Wheel of Life approach. Both systems start with goals and tasks to achieve them. Then start executing on a realistic timeline.
If you find solutions, weaknesses don't matter.
Everyone's weak. You, me, Gates, Dalio, even Musk. Nobody will be great at all 5 steps of the system because no one can think in all the ways required. Some are good at analyzing and diagnosing but bad at executing. Some are good planners but poor communicators. Others lack self-discipline.
Stay humble and ask for help when needed. Nobody has ever succeeded 100% on their own, without anyone else's help. That's the paradox of individual success: teamwork is the only way to get there.
Most people won't have the skills to execute even the best plan. You can get missing skills in two ways:
Self-taught (time-consuming)
Others' (requires humility) light
On knowing what to do with your life
“Some people have good mental maps and know what to do on their own. Maybe they learned them or were blessed with common sense. They have more answers than others. Others are more humble and open-minded. […] Open-mindedness and mental maps are most powerful.” — Ray Dalio
I've always known what I wanted to do, so I'm lucky. I'm almost 30 and have always had trouble executing. Good thing I never stopped experimenting, but I never committed to anything long-term. I jumped between projects. I decided 3 years ago to stick to one project for at least 6 months and haven't looked back.
Maybe you're good at staying focused and executing, but you don't know what to do. Maybe you have none of these because you haven't found your purpose. Always try new projects and talk to as many people as possible. It will give you inspiration and ideas and set you up for success.
There is almost always a way to achieve a crazy goal or idea.
Enjoy the journey, whichever path you take.
