More on Economics & Investing
Sam Hickmann
3 years ago
What is this Fed interest rate everybody is talking about that makes or breaks the stock market?
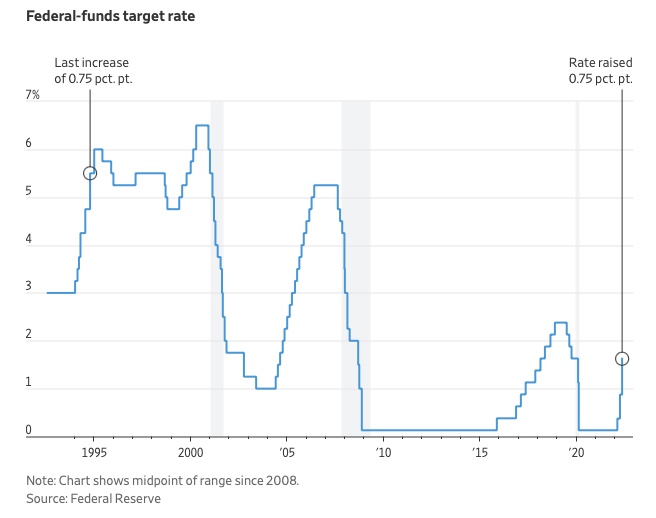
The Federal Funds Rate (FFR) is the target interest rate set by the Federal Reserve System (Fed)'s policy-making body (FOMC). This target is the rate at which the Fed suggests commercial banks borrow and lend their excess reserves overnight to each other.
The FOMC meets 8 times a year to set the target FFR. This is supposed to promote economic growth. The overnight lending market sets the actual rate based on commercial banks' short-term reserves. If the market strays too far, the Fed intervenes.
Banks must keep a certain percentage of their deposits in a Federal Reserve account. A bank's reserve requirement is a percentage of its total deposits. End-of-day bank account balances averaged over two-week reserve maintenance periods are used to determine reserve requirements.
If a bank expects to have end-of-day balances above what's needed, it can lend the excess to another institution.
The FOMC adjusts interest rates based on economic indicators that show inflation, recession, or other issues that affect economic growth. Core inflation and durable goods orders are indicators.
In response to economic conditions, the FFR target has changed over time. In the early 1980s, inflation pushed it to 20%. During the Great Recession of 2007-2009, the rate was slashed to 0.15 percent to encourage growth.
Inflation picked up in May 2022 despite earlier rate hikes, prompting today's 0.75 percent point increase. The largest increase since 1994. It might rise to around 3.375% this year and 3.1% by the end of 2024.

Cory Doctorow
3 years ago
The current inflation is unique.
New Stiglitz just dropped.

Here's the inflation story everyone believes (warning: it's false): America gave the poor too much money during the recession, and now the economy is awash with free money, which made them so rich they're refusing to work, meaning the economy isn't making anything. Prices are soaring due to increased cash and missing labor.
Lawrence Summers says there's only one answer. We must impoverish the poor: raise interest rates, cause a recession, and eliminate millions of jobs, until the poor are stripped of their underserved fortunes and return to work.
https://pluralistic.net/2021/11/20/quiet-part-out-loud/#profiteering
This is nonsense. Countries around the world suffered inflation during and after lockdowns, whether they gave out humanitarian money to keep people from starvation. America has slightly greater inflation than other OECD countries, but it's not due to big relief packages.
The Causes of and Responses to Today's Inflation, a Roosevelt Institute report by Nobel-winning economist Joseph Stiglitz and macroeconomist Regmi Ira, debunks this bogus inflation story and offers a more credible explanation for inflation.
https://rooseveltinstitute.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/RI CausesofandResponsestoTodaysInflation Report 202212.pdf
Sharp interest rate hikes exacerbate the slump and increase inflation, the authors argue. They compare monetary policy inflation cures to medieval bloodletting, where doctors repeated the same treatment until the patient recovered (for which they received credit) or died (which was more likely).
Let's discuss bloodletting. Inflation hawks warn of the wage price spiral, when inflation rises and powerful workers bargain for higher pay, driving up expenses, prices, and wages. This is the fairy-tale narrative of the 1970s, and it's true except that OPEC's embargo drove up oil prices, which produced inflation. Oh well.
Let's be generous to seventies-haunted inflation hawks and say we're worried about a wage-price spiral. Fantastic! No. Real wages are 2.3% lower than they were in Oct 2021 after peaking in June at 4.8%.
Why did America's powerful workers take a paycut rather than demand inflation-based pay? Weak unions, globalization, economic developments.
Workers don't expect inflation to rise, so they're not requesting inflationary hikes. Inflationary expectations have remained moderate, consistent with our data interpretation.
https://www.newyorkfed.org/microeconomics/sce#/
Neither are workers. Working people see surplus savings as wealth and spend it gradually over their lives, despite rising demand. People may have saved money by staying in during the lockdown, but they don't eat out every night to make up for it. Instead, they keep those savings as precautionary balances. This is why the economy is lagging.
People don't buy non-traded goods with pandemic savings (basically, imports). Imports don't multiply like domestic purchases. If you buy a loaf of bread from the corner baker for $1 and they spend it at the tavern across the street, that dollar generates $3 in economic activity. Spending a dollar on foreign goods leaves the country and any multiplier effect happens there, not in the US.
Only marginally higher wages. The ECI is up 1.6% from 2019. Almost all gains went to the 25% lowest-paid Americans. Contrary to the inflation worry about too much savings, these workers don't make enough to save, even post-pandemic.
Recreation and transit spending are at or below pre-pandemic levels. Higher food and hotel prices (which doesn’t mean we’re buying more food than we were in 2019, just that it costs more).
What causes inflation if not greedy workers, free money, and high demand? The most expensive domestic goods produce the biggest revenues for their manufacturers. They charge you more without paying their workers or suppliers more.
The largest price-gougers are funneling their earnings to rich people who store it offshore through stock buybacks and dividends. A $1 billion stock buyback doesn't buy $1 billion in bread.
Five factors influence US inflation today:
I. Price rises for energy and food
II. shifts in consumer tastes
III. supply interruptions (mainly autos);
IV. increased rents (due to telecommuting);
V. monopoly (AKA price-gouging).
None can be remedied by raising interest rates or laying off workers.
Russia's invasion of Ukraine, omicron, and China's Zero Covid policy all disrupted the flow of food, energy, and production inputs. The price went higher because we made less.
After Russia invaded Ukraine, oil prices spiked, and sanctions made it worse. But that was February. By October, oil prices had returned to pre-pandemic, 2015 levels attributable to global economic adjustments, including a shift to renewables. Every new renewable installation reduces oil consumption and affects oil prices.
High food prices have a simple solution. The US and EU have bribed farmers not to produce for 50 years. If the war continues, this program may end, and food prices may decline.
Demand changes. We want different things than in 2019, not more. During the lockdown, people substituted goods. Half of the US toilet-paper supply in 2019 was on commercial-sized rolls. This is created from different mills and stock than our toilet paper.
Lockdown pushed toilet paper demand to residential rolls, causing shortages (the TP hoarding story was just another pandemic urban legend). Because supermarket stores don't have accounts with commercial paper distributors, ordering from languishing stores was difficult. Kleenex and paper towel substitutions caused greater shortages.
All that drove increased costs in numerous product categories, and there were more cases. These increases are transient, caused by supply chain inefficiencies that are resolving.
Demand for frontline staff saw a one-time repricing of pay, which is being recouped as we speak.
Illnesses. Brittle, hollowed-out global supply chains aggravated this. The constant pursuit of cheap labor and minimal regulation by monopolies that dominate most sectors means things are manufactured in far-flung locations. Financialization means any surplus capital assets were sold off years ago, leaving firms with little production slack. After the epidemic, several of these systems took years to restart.
Automobiles are to blame. Financialization and monopolization consolidated microchip and auto production in Taiwan and China. When the lockdowns came, these worldwide corporations cancelled their chip orders, and when they placed fresh orders, they were at the back of the line.
That drove up car prices, which is why the US has slightly higher inflation than other wealthy countries: the economy is car-centric. Automobile prices account for 9% of the CPI. France: 3.6%
Rent shocks and telecommuting. After the epidemic, many professionals moved to exurbs, small towns, and the countryside to work from home. As commercial properties were vacated, it was impractical to adapt them for residential use due to planning restrictions. Addressing these restrictions will cut rent prices more than raising inflation rates, which halts housing construction.
Statistical mirages cause some rent inflation. The CPI estimates what homeowners would pay to rent their properties. When rents rise in your neighborhood, the CPI believes you're spending more on rent even if you have a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage.
Market dominance. Almost every area of the US economy is dominated by monopolies, whose CEOs disclose on investor calls that they use inflation scares to jack up prices and make record profits.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/02/02/its-the-economy-stupid/#overinflated
Long-term profit margins are rising. Markups averaged 26% from 1960-1980. 2021: 72%. Market concentration explains 81% of markup increases (e.g. monopolization). Profit margins reach a 70-year high in 2022. These elements interact. Monopolies thin out their sectors, making them brittle and sensitive to shocks.
If we're worried about a shrinking workforce, there are more humanitarian and sensible solutions than causing a recession and mass unemployment. Instead, we may boost US production capacity by easing workers' entry into the workforce.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/06/01/factories-to-condos-pipeline/#stuff-not-money
US female workforce participation ranks towards the bottom of developed countries. Many women can't afford to work due to America's lack of daycare, low earnings, and bad working conditions in female-dominated fields. If America doesn't have enough workers, childcare subsidies and minimum wages can help.
By contrast, driving the country into recession with interest-rate hikes will reduce employment, and the last recruited (women, minorities) are the first fired and the last to be rehired. Forcing America into recession won't enhance its capacity to create what its people want; it will degrade it permanently.
Nothing the Fed does can stop price hikes from international markets, lack of supply chain investment, COVID-19 disruptions, climate change, the Ukraine war, or market power. They can worsen it. When supply problems generate inflation, raising interest rates decreases investments that can remedy shortages.
Increasing interest rates won't cut rents since landlords pass on the expenses and high rates restrict investment in new dwellings where tenants could escape the costs.
Fixing the supply fixes supply-side inflation. Increase renewables investment (as the Inflation Reduction Act does). Monopolies can be busted (as the IRA does). Reshore key goods (as the CHIPS Act does). Better pay and child care attract employees.
Windfall taxes can claw back price-gouging corporations' monopoly earnings.
https://pluralistic.net/2022/03/15/sanctions-financing/#soak-the-rich
In 2008, we ruled out fiscal solutions (bailouts for debtors) and turned to monetary policy (bank bailouts). This preserved the economy but increased inequality and eroded public trust.
Monetary policy won't help. Even monetary policy enthusiasts recognize an 18-month lag between action and result. That suggests monetary tightening is unnecessary. Like the medieval bloodletter, central bankers whose interest rate hikes don't work swiftly may do more of the same, bringing the economy to its knees.
Interest rates must rise. Zero-percent interest fueled foolish speculation and financialization. Increasing rates will stop this. Increasing interest rates will destroy the economy and dampen inflation.
Then what? All recent evidence indicate to inflation decreasing on its own, as the authors argue. Supply side difficulties are finally being overcome, evidence shows. Energy and food prices are showing considerable mean reversion, which is disinflationary.
The authors don't recommend doing nothing. Best case scenario, they argue, is that the Fed won't keep raising interest rates until morale improves.
Sam Hickmann
3 years ago
What is headline inflation?
Headline inflation is the raw Consumer price index (CPI) reported monthly by the Bureau of labour statistics (BLS). CPI measures inflation by calculating the cost of a fixed basket of goods. The CPI uses a base year to index the current year's prices.
Explaining Inflation
As it includes all aspects of an economy that experience inflation, headline inflation is not adjusted to remove volatile figures. Headline inflation is often linked to cost-of-living changes, which is useful for consumers.
The headline figure doesn't account for seasonality or volatile food and energy prices, which are removed from the core CPI. Headline inflation is usually annualized, so a monthly headline figure of 4% inflation would equal 4% inflation for the year if repeated for 12 months. Top-line inflation is compared year-over-year.
Inflation's downsides
Inflation erodes future dollar values, can stifle economic growth, and can raise interest rates. Core inflation is often considered a better metric than headline inflation. Investors and economists use headline and core results to set growth forecasts and monetary policy.
Core Inflation
Core inflation removes volatile CPI components that can distort the headline number. Food and energy costs are commonly removed. Environmental shifts that affect crop growth can affect food prices outside of the economy. Political dissent can affect energy costs, such as oil production.
From 1957 to 2018, the U.S. averaged 3.64 percent core inflation. In June 1980, the rate reached 13.60%. May 1957 had 0% inflation. The Fed's core inflation target for 2022 is 3%.
Central bank:
A central bank has privileged control over a nation's or group's money and credit. Modern central banks are responsible for monetary policy and bank regulation. Central banks are anti-competitive and non-market-based. Many central banks are not government agencies and are therefore considered politically independent. Even if a central bank isn't government-owned, its privileges are protected by law. A central bank's legal monopoly status gives it the right to issue banknotes and cash. Private commercial banks can only issue demand deposits.
What are living costs?
The cost of living is the amount needed to cover housing, food, taxes, and healthcare in a certain place and time. Cost of living is used to compare the cost of living between cities and is tied to wages. If expenses are higher in a city like New York, salaries must be higher so people can live there.
What's U.S. bureau of labor statistics?
BLS collects and distributes economic and labor market data about the U.S. Its reports include the CPI and PPI, both important inflation measures.
You might also like

Architectural Digest
3 years ago
Take a look at The One, a Los Angeles estate with a whopping 105,000 square feet of living area.
The interiors of the 105,000-square-foot property, which sits on a five-acre parcel in the wealthy Los Angeles suburb of Bel Air and is suitably titled The One, have been a well guarded secret. We got an intimate look inside this world-record-breaking property, as well as the creative and aesthetic geniuses behind it.
The estate appears to float above the city, surrounded on three sides by a moat and a 400-foot-long running track. Completed over eight years—and requiring 600 workers to build—the home was designed by architect Paul McClean and interior designer Kathryn Rotondi, who were enlisted by owner and developer Nile Niami to help it live up to its standard.
"This endeavor seemed both exhilarating and daunting," McClean says. However, the home's remarkable location and McClean's long-standing relationship with Niami persuaded him to "build something unique and extraordinary" rather than just take on the job.
And McClean has more than delivered.
The home's main entrance leads to a variety of meeting places with magnificent 360-degree views of the Pacific Ocean, downtown Los Angeles, and the San Gabriel Mountains, thanks to its 26-foot-high ceilings. There is water at the entrance area, as well as a sculpture and a bridge. "We often employ water in our design approach because it provides a sensory change that helps you acclimatize to your environment," McClean explains.
Niami wanted a neutral palette that would enable the environment and vistas to shine, so she used black, white, and gray throughout the house.
McClean has combined the home's inside with outside "to create that quintessential L.A. lifestyle but on a larger scale," he says, drawing influence from the local environment and history of Los Angeles modernism. "We separated the entertaining spaces from the living portions to make the house feel more livable. The former are on the lowest level, which serves as a plinth for the rest of the house and minimizes its apparent mass."
The home's statistics, in addition to its eye-catching style, are equally impressive. There are 42 bathrooms, 21 bedrooms, a 5,500-square-foot master suite, a 30-car garage gallery with two car-display turntables, a four-lane bowling alley, a spa level, a 30-seat movie theater, a "philanthropy wing (with a capacity of 200) for charity galas, a 10,000-square-foot sky deck, and five swimming pools.
Rotondi, the creator of KFR Design, collaborated with Niami on the interior design to create different spaces that flow into one another despite the house's grandeur. "I was especially driven to 'wow factor' components in the hospitality business," Rotondi says, citing top luxury hotel brands such as Aman, Bulgari, and Baccarat as sources of inspiration. Meanwhile, the home's color scheme, soft textures, and lighting are a nod to Niami and McClean's favorite Tom Ford boutique on Rodeo Drive.
The house boasts an extraordinary collection of art, including a butterfly work by Stephen Wilson on the lower level and a Niclas Castello bespoke panel in black and silver in the office, thanks to a cooperation between Creative Art Partners and Art Angels. There is also a sizable collection of bespoke furniture pieces from byShowroom.
A house of this size will never be erected again in Los Angeles, thanks to recently enacted city rules, so The One will truly be one of a kind. "For all of us, this project has been such a long and instructive trip," McClean says. "It was exciting to develop and approached with excitement, but I don't think any of us knew how much effort and time it would take to finish the project."

Pat Vieljeux
3 years ago
In 5 minutes, you can tell if a startup will succeed.
Or the “lie to me” method.

I can predict a startup's success in minutes.
Just interview its founder.
Ask "why?"
I question "why" till I sense him.
I need to feel the person I have in front of me. I need to know if he or she can deliver. Startups aren't easy. Without abilities, a brilliant idea will fail.
Good entrepreneurs have these qualities: He's a leader, determined, and resilient.
For me, they can be split in two categories.
The first entrepreneur aspires to live meaningfully. The second wants to get rich. The second is communicative. He wants to wow the crowd. He's motivated by the thought of one day sailing a boat past palm trees and sunny beaches.
What drives the first entrepreneur is evident in his speech, face, and voice. He will not speak about his product. He's (nearly) uninterested. He's not selling anything. He's not a salesman. He wants to succeed. The product is his fuel.
He'll explain his decision. He'll share his motivations. His desire. And he'll use meaningful words.
Paul Ekman has shown that face expressions aren't cultural. His study influenced the American TV series "lie to me" about body language and speech.
Passionate entrepreneurs are obvious. It's palpable. Faking passion is tough. Someone who wants your favor and money will expose his actual motives through his expressions and language.
The good liar will be able to fool you for a while, but not for long if you pay attention to his body language and how he expresses himself.
And also, if you look at his business plan.
His business plan reveals his goals. Read between the lines.
Entrepreneur 1 will focus on his "why", whereas Entrepreneur 2 will focus on the "how".
Entrepreneur 1 will develop a vision-driven culture.
The second, on the other hand, will focus on his EBITDA.
Why is the culture so critical? Because it will allow entrepreneur 1 to develop a solid team that can tackle his problems and trials. His team's "why" will keep them together in tough times.
"Give me a terrific start-up team with a mediocre idea over a weak one any day." Because a great team knows when to pivot and trusts each other. Weak teams fail.” — Bernhard Schroeder
Closings thoughts
Every VC must ask Why. Entrepreneur's motivations. This "why" will create the team's culture. This culture will help the team adjust to any setback.

ANDREW SINGER
3 years ago
Crypto seen as the ‘future of money’ in inflation-mired countries
Crypto as the ‘future of money' in inflation-stricken nations
Citizens of devalued currencies “need” crypto. “Nice to have” in the developed world.
According to Gemini's 2022 Global State of Crypto report, cryptocurrencies “evolved from what many considered a niche investment into an established asset class” last year.
More than half of crypto owners in Brazil (51%), Hong Kong (51%), and India (54%), according to the report, bought cryptocurrency for the first time in 2021.
The study found that inflation and currency devaluation are powerful drivers of crypto adoption, especially in emerging market (EM) countries:
“Respondents in countries that have seen a 50% or greater devaluation of their currency against the USD over the last decade were more than 5 times as likely to plan to purchase crypto in the coming year.”
Between 2011 and 2021, the real lost 218 percent of its value against the dollar, and 45 percent of Brazilians surveyed by Gemini said they planned to buy crypto in 2019.
The rand (South Africa's currency) has fallen 103 percent in value over the last decade, second only to the Brazilian real, and 32 percent of South Africans expect to own crypto in the coming year. Mexico and India, the third and fourth highest devaluation countries, followed suit.
Compared to the US dollar, Hong Kong and the UK currencies have not devalued in the last decade. Meanwhile, only 5% and 8% of those surveyed in those countries expressed interest in buying crypto.
What can be concluded? Noah Perlman, COO of Gemini, sees various crypto use cases depending on one's location.
‘Need to have' investment in countries where the local currency has devalued against the dollar, whereas in the developed world it is still seen as a ‘nice to have'.
Crypto as money substitute
As an adjunct professor at New York University School of Law, Winston Ma distinguishes between an asset used as an inflation hedge and one used as a currency replacement.
Unlike gold, he believes Bitcoin (BTC) is not a “inflation hedge”. They acted more like growth stocks in 2022. “Bitcoin correlated more closely with the S&P 500 index — and Ether with the NASDAQ — than gold,” he told Cointelegraph. But in the developing world, things are different:
“Inflation may be a primary driver of cryptocurrency adoption in emerging markets like Brazil, India, and Mexico.”
According to Justin d'Anethan, institutional sales director at the Amber Group, a Singapore-based digital asset firm, early adoption was driven by countries where currency stability and/or access to proper banking services were issues. Simply put, he said, developing countries want alternatives to easily debased fiat currencies.
“The larger flows may still come from institutions and developed countries, but the actual users may come from places like Lebanon, Turkey, Venezuela, and Indonesia.”
“Inflation is one of the factors that has and continues to drive adoption of Bitcoin and other crypto assets globally,” said Sean Stein Smith, assistant professor of economics and business at Lehman College.
But it's only one factor, and different regions have different factors, says Stein Smith. As a “instantaneously accessible, traceable, and cost-effective transaction option,” investors and entrepreneurs increasingly recognize the benefits of crypto assets. Other places promote crypto adoption due to “potential capital gains and returns”.
According to the report, “legal uncertainty around cryptocurrency,” tax questions, and a general education deficit could hinder adoption in Asia Pacific and Latin America. In Africa, 56% of respondents said more educational resources were needed to explain cryptocurrencies.
Not only inflation, but empowering our youth to live better than their parents without fear of failure or allegiance to legacy financial markets or products, said Monica Singer, ConsenSys South Africa lead. Also, “the issue of cash and remittances is huge in Africa, as is the issue of social grants.”
Money's future?
The survey found that Brazil and Indonesia had the most cryptocurrency ownership. In each country, 41% of those polled said they owned crypto. Only 20% of Americans surveyed said they owned cryptocurrency.
These markets are more likely to see cryptocurrencies as the future of money. The survey found:
“The majority of respondents in Latin America (59%) and Africa (58%) say crypto is the future of money.”
Brazil (66%), Nigeria (63%), Indonesia (61%), and South Africa (57%). Europe and Australia had the fewest believers, with Denmark at 12%, Norway at 15%, and Australia at 17%.
Will the Ukraine conflict impact adoption?
The poll was taken before the war. Will the devastating conflict slow global crypto adoption growth?
With over $100 million in crypto donations directly requested by the Ukrainian government since the war began, Stein Smith says the war has certainly brought crypto into the mainstream conversation.
“This real-world demonstration of decentralized money's power could spur wider adoption, policy debate, and increased use of crypto as a medium of exchange.”
But the war may not affect all developing nations. “The Ukraine war has no impact on African demand for crypto,” Others loom larger. “Yes, inflation, but also a lack of trust in government in many African countries, and a young demographic very familiar with mobile phones and the internet.”
A major success story like Mpesa in Kenya has influenced the continent and may help accelerate crypto adoption. Creating a plan when everyone you trust fails you is directly related to the African spirit, she said.
On the other hand, Ma views the Ukraine conflict as a sort of crisis check for cryptocurrencies. For those in emerging markets, the Ukraine-Russia war has served as a “stress test” for the cryptocurrency payment rail, he told Cointelegraph.
“These emerging markets may see the greatest future gains in crypto adoption.”
Inflation and currency devaluation are persistent global concerns. In such places, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are now seen as the “future of money.” Not in the developed world, but that could change with better regulation and education. Inflation and its impact on cash holdings are waking up even Western nations.
Read original post here.
