More on Marketing

Saskia Ketz
2 years ago
I hate marketing for my business, but here's how I push myself to keep going
Start now.

When it comes to building my business, I’m passionate about a lot of things. I love creating user experiences that simplify branding essentials. I love creating new typefaces and color combinations to inspire logo designers. I love fixing problems to improve my product.
Business marketing isn't my thing.
This is shared by many. Many solopreneurs, like me, struggle to advertise their business and drive themselves to work on it.
Without a lot of promotion, no company will succeed. Marketing is 80% of developing a firm, and when you're starting out, it's even more. Some believe that you shouldn't build anything until you've begun marketing your idea and found enough buyers.
Marketing your business without marketing experience is difficult. There are various outlets and techniques to learn. Instead of figuring out where to start, it's easier to return to your area of expertise, whether that's writing, designing product features, or improving your site's back end. Right?
First, realize that your role as a founder is to market your firm. Being a founder focused on product, I rarely work on it.
Secondly, use these basic methods that have helped me dedicate adequate time and focus to marketing. They're all simple to apply, and they've increased my business's visibility and success.
1. Establish buckets for every task.
You've probably heard to schedule tasks you don't like. As simple as it sounds, blocking a substantial piece of my workday for marketing duties like LinkedIn or Twitter outreach, AppSumo customer support, or SEO has forced me to spend time on them.
Giving me lots of room to focus on product development has helped even more. Sure, this means scheduling time to work on product enhancements after my four-hour marketing sprint.

It also involves making space to store product inspiration and ideas throughout the day so I don't get distracted. This is like the advice to keep a notebook beside your bed to write down your insomniac ideas. I keep fonts, color palettes, and product ideas in folders on my desktop. Knowing these concepts won't be lost lets me focus on marketing in the moment. When I have limited time to work on something, I don't have to conduct the research I've been collecting, so I can get more done faster.

2. Look for various accountability systems
Accountability is essential for self-discipline. To keep focused on my marketing tasks, I've needed various streams of accountability, big and little.
Accountability groups are great for bigger things. SaaS Camp, a sales outreach coaching program, is mine. We discuss marketing duties and results every week. This motivates me to do enough each week to be proud of my accomplishments. Yet hearing what works (or doesn't) for others gives me benchmarks for my own marketing outcomes and plenty of fresh techniques to attempt.
… say, I want to DM 50 people on Twitter about my product — I get that many Q-tips and place them in one pen holder on my desk.
The best accountability group can't watch you 24/7. I use a friend's simple method that shouldn't work (but it does). When I have a lot of marketing chores, like DMing 50 Twitter users about my product, That many Q-tips go in my desk pen holder. After each task, I relocate one Q-tip to an empty pen holder. When you have a lot of minor jobs to perform, it helps to see your progress. You might use toothpicks, M&Ms, or anything else you have a lot of.

3. Continue to monitor your feedback loops
Knowing which marketing methods work best requires monitoring results. As an entrepreneur with little go-to-market expertise, every tactic I pursue is an experiment. I need to know how each trial is doing to maximize my time.
I placed Google and Facebook advertisements on hold since they took too much time and money to obtain Return. LinkedIn outreach has been invaluable to me. I feel that talking to potential consumers one-on-one is the fastest method to grasp their problem areas, figure out my messaging, and find product market fit.
Data proximity offers another benefit. Seeing positive results makes it simpler to maintain doing a work you don't like. Why every fitness program tracks progress.
Marketing's goal is to increase customers and revenues, therefore I've found it helpful to track those metrics and celebrate monthly advances. I provide these updates for extra accountability.
Finding faster feedback loops is also motivating. Marketing brings more clients and feedback, in my opinion. Product-focused founders love that feedback. Positive reviews make me proud that my product is benefitting others, while negative ones provide me with suggestions for product changes that can improve my business.
The best advice I can give a lone creator who's afraid of marketing is to just start. Start early to learn by doing and reduce marketing stress. Start early to develop habits and successes that will keep you going. The sooner you start, the sooner you'll have enough consumers to return to your favorite work.

Yucel F. Sahan
3 years ago
How I Created the Day's Top Product on Product Hunt
In this article, I'll describe a weekend project I started to make something. It was Product Hunt's #1 of the Day, #2 Weekly, and #4 Monthly product.


How did I make Landing Page Checklist so simple? Building and launching took 3 weeks. I worked 3 hours a day max. Weekends were busy.
It's sort of a long story, so scroll to the bottom of the page to see what tools I utilized to create Landing Page Checklist :x
As a matter of fact, it all started with the startups-investments blog; Startup Bulletin, that I started writing in 2018. No, don’t worry, I won’t be going that far behind. The twitter account where I shared the blog posts of this newsletter was inactive for a looong time. I was holding this Twitter account since 2009, I couldn’t bear to destroy it. At the same time, I was thinking how to evaluate this account.
So I looked for a weekend assignment.

Weekend undertaking: Generate business names
Barash and I established a weekend effort to stay current. Building things helped us learn faster.
Simple. Startup Name Generator The utility generated random startup names. After market research for SEO purposes, we dubbed it Business Name Generator.
Backend developer Barash dislikes frontend work. He told me to write frontend code. Chakra UI and Tailwind CSS were recommended.
It was the first time I have heard about Tailwind CSS.
Before this project, I made mobile-web app designs in Sketch and shared them via Zeplin. I can read HTML-CSS or React code, but not write it. I didn't believe myself but followed Barash's advice.
My home page wasn't responsive when I started. Here it was:)

And then... Product Hunt had something I needed. Me-only! A website builder that gives you clean Tailwind CSS code and pre-made web components (like Elementor). Incredible.
I bought it right away because it was so easy to use. Best part: It's not just index.html. It includes all needed files. Like
postcss.config.js
README.md
package.json
among other things, tailwind.config.js

This is for non-techies.
Tailwind.build; which is Shuffle now, allows you to create and export projects for free (with limited features). You can try it by visiting their website.
After downloading the project, you can edit the text and graphics in Visual Studio (or another text editor). This HTML file can be hosted whenever.
Github is an easy way to host a landing page.
your project via Shuffle for export
your website's content, edit
Create a Gitlab, Github, or Bitbucket account.
to Github, upload your project folder.
Integrate Vercel with your Github account (or another platform below)
Allow them to guide you in steps.
Finally. If you push your code to Github using Github Desktop, you'll do it quickly and easily.
Speaking of; here are some hosting and serverless backend services for web applications and static websites for you host your landing pages for FREE!
I host landingpage.fyi on Vercel but all is fine. You can choose any platform below with peace in mind.
Vercel
Render
Netlify
After connecting your project/repo to Vercel, you don’t have to do anything on Vercel. Vercel updates your live website when you update Github Desktop. Wow!
Tails came out while I was using tailwind.build. Although it's prettier, tailwind.build is more mobile-friendly. I couldn't resist their lovely parts. Tails :)
Tails have several well-designed parts. Some components looked awful on mobile, but this bug helped me understand Tailwind CSS.
Unlike Shuffle, Tails does not include files when you export such as config.js, main.js, README.md. It just gives you the HTML code. Suffle.dev is a bit ahead in this regard and with mobile-friendly blocks if you ask me. Of course, I took advantage of both.
creativebusinessnames.co is inactive, but I'll leave a deployment link :)
Adam Wathan's YouTube videos and Tailwind's official literature helped me, but I couldn't have done it without Tails and Shuffle. These tools helped me make landing pages. I shouldn't have started over.
So began my Tailwind CSS adventure. I didn't build landingpage. I didn't plan it to be this long; sorry.
I learnt a lot while I was playing around with Shuffle and Tails Builders.
Long story short I built landingpage.fyi with the help of these tools;
Learning, building, and distribution
Shuffle (Started with a Shuffle Template)
Tails (Used components from here)
Sketch (to handle icons, logos, and .svg’s)
metatags.io (Auto Generator Meta Tags)
Vercel (Hosting)
Github Desktop (Pushing code to Github -super easy-)
Visual Studio Code (Edit my code)
Mailerlite (Capture Emails)
Jarvis / Conversion.ai (%90 of the text on website written by AI 😇 )
CookieHub (Consent Management)
That's all. A few things:
The Outcome

.fyi Domain: Why?

I'm often asked this.
I don't know, but I wanted to include the landing page term. Popular TLDs are gone. I saw my alternatives. brief and catchy.
CSS Tailwind Resources
I'll share project resources like Tails and Shuffle.
Beginner Tailwind (I lately enrolled in this course but haven’t completed it yet.)
Thanks for reading my blog's first post. Please share if you like it.

Camilla Dudley
3 years ago
How to gain Twitter followers: A 101 Guide

No wonder brands use Twitter to reach their audience. 53% of Twitter users buy new products first.
Twitter growth does more than make your brand look popular. It helps clients trust your business. It boosts your industry standing. It shows clients, prospects, and even competitors you mean business.
How can you naturally gain Twitter followers?
Share useful information
Post visual content
Tweet consistently
Socialize
Spread your @name everywhere.
Use existing customers
Promote followers
Share useful information
Twitter users join conversations and consume material. To build your followers, make sure your material appeals to them and gives value, whether it's sales, product lessons, or current events.
Use Twitter Analytics to learn what your audience likes.
Explore popular topics by utilizing relevant keywords and hashtags. Check out this post on how to use Twitter trends.
Post visual content
97% of Twitter users focus on images, so incorporating media can help your Tweets stand out. Visuals and videos make content more engaging and memorable.
Tweet often
Your audience should expect regular content updates. Plan your ideas and tweet during crucial seasons and events with a content calendar.
Socialize
Twitter connects people. Do more than tweet. Follow industry leaders. Retweet influencers, engage with thought leaders, and reply to mentions and customers to boost engagement.
Micro-influencers can promote your brand or items. They can help you gain new audiences' trust.
Spread your @name everywhere.
Maximize brand exposure. Add a follow button on your website, link to it in your email signature and newsletters, and promote it on business cards or menus.
Use existing customers
Emails can be used to find existing Twitter clients. Upload your email contacts and follow your customers on Twitter to start a dialogue.
Promote followers
Run a followers campaign to boost your organic growth. Followers campaigns promote your account to a particular demographic, and you only pay when someone follows you.
Consider short campaigns to enhance momentum or an always-on campaign to gain new followers.
Increasing your brand's Twitter followers takes effort and experimentation, but the payback is huge.
👋 Follow me on twitter
You might also like

Elnaz Sarraf
3 years ago
Why Bitcoin's Crash Could Be Good for Investors

The crypto market crashed in June 2022. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies hit their lowest prices in over a year, causing market panic. Some believe this crash will benefit future investors.
Before I discuss how this crash might help investors, let's examine why it happened. Inflation in the U.S. reached a 30-year high in 2022 after Russia invaded Ukraine. In response, the U.S. Federal Reserve raised interest rates by 0.5%, the most in almost 20 years. This hurts cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Higher interest rates make people less likely to invest in volatile assets like crypto, so many investors sold quickly.
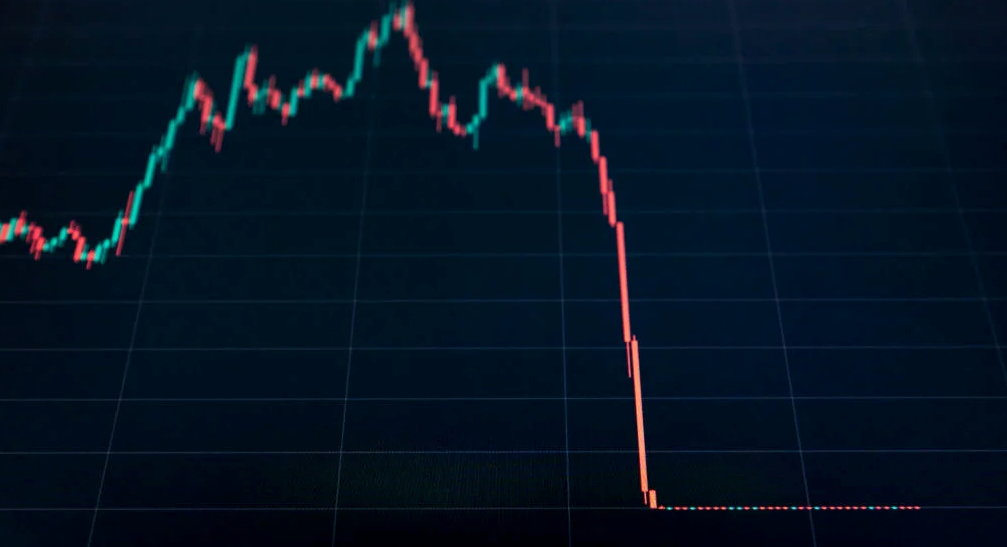
The crypto market collapsed. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Binance dropped 40%. Other cryptos crashed so hard they were delisted from almost every exchange. Bitcoin peaked in April 2022 at $41,000, but after the May interest rate hike, it crashed to $28,000. Bitcoin investors were worried. Even in bad times, this crash is unprecedented.
Bitcoin wasn't "doomed." Before the crash, LUNA was one of the top 5 cryptos by market cap. LUNA was trading around $80 at the start of May 2022, but after the rate hike?
Less than 1 cent. LUNA lost 99.99% of its value in days and was removed from every crypto exchange. Bitcoin's "crash" isn't as devastating when compared to LUNA.
Many people said Bitcoin is "due" for a LUNA-like crash and that the only reason it hasn't crashed is because it's bigger. Still false. If so, Bitcoin should be worth zero by now. We didn't. Instead, Bitcoin reached 28,000, then 29k, 30k, and 31k before falling to 18k. That's not the world's greatest recovery, but it shows Bitcoin's safety.
Bitcoin isn't falling constantly. It fell because of the initial shock of interest rates, but not further. Now, Bitcoin's value is more likely to rise than fall. Bitcoin's low price also attracts investors. They know what prices Bitcoin can reach with enough hype, and they want to capitalize on low prices before it's too late.

Bitcoin's crash was bad, but in a way it wasn't. To understand, consider 2021. In March 2021, Bitcoin surpassed $60k for the first time. Elon Musk's announcement in May that he would no longer support Bitcoin caused a massive crash in the crypto market. In May 2017, Bitcoin's price hit $29,000. Elon Musk's statement isn't worth more than the Fed raising rates. Many expected this big announcement to kill Bitcoin.

Not so. Bitcoin crashed from $58k to $31k in 2021. Bitcoin fell from $41k to $28k in 2022. This crash is smaller. Bitcoin's price held up despite tensions and stress, proving investors still believe in it. What happened after the initial crash in the past?
Bitcoin fell until mid-July. This is also something we’re not seeing today. After a week, Bitcoin began to improve daily. Bitcoin's price rose after mid-July. Bitcoin's price fluctuated throughout the rest of 2021, but it topped $67k in November. Despite no major changes, the peak occurred after the crash. Elon Musk seemed uninterested in crypto and wasn't likely to change his mind soon. What triggered this peak? Nothing, really. What really happened is that people got over the initial statement. They forgot.
Internet users have goldfish-like attention spans. People quickly forgot the crash's cause and were back investing in crypto months later. Despite the market's setbacks, more crypto investors emerged by the end of 2017. Who gained from these peaks? Bitcoin investors who bought low. Bitcoin not only recovered but also doubled its ROI. It was like a movie, and it shows us what to expect from Bitcoin in the coming months.
The current Bitcoin crash isn't as bad as the last one. LUNA is causing market panic. LUNA and Bitcoin are different cryptocurrencies. LUNA crashed because Terra wasn’t able to keep its peg with the USD. Bitcoin is unanchored. It's one of the most decentralized investments available. LUNA's distrust affected crypto prices, including Bitcoin, but it won't last forever.
This is why Bitcoin will likely rebound in the coming months. In 2022, people will get over the rise in interest rates and the crash of LUNA, just as they did with Elon Musk's crypto stance in 2021. When the world moves on to the next big controversy, Bitcoin's price will soar.
Bitcoin may recover for another reason. Like controversy, interest rates fluctuate. The Russian invasion caused this inflation. World markets will stabilize, prices will fall, and interest rates will drop.
Next, lower interest rates could boost Bitcoin's price. Eventually, it will happen. The U.S. economy can't sustain such high interest rates. Investors will put every last dollar into Bitcoin if interest rates fall again.
Bitcoin has proven to be a stable investment. This boosts its investment reputation. Even if Ethereum dethrones Bitcoin as crypto king one day (or any other crypto, for that matter). Bitcoin may stay on top of the crypto ladder for a while. We'll have to wait a few months to see if any of this is true.
This post is a summary. Read the full article here.
Hannah Elliott
3 years ago
Pebble Beach Auto Auctions Set $469M Record
The world's most prestigious vintage vehicle show included amazing autos and record-breaking sums.

This 1932 Duesenberg J Figoni Sports Torpedo earned Best of Show in 2022.
David Paul Morris (DPM)/Bloomberg
2022 Pebble Beach Concours d'Elegance winner was a pre-war roadster.
Lee Anderson's 1932 Duesenberg J Figoni Sports Torpedo won Best of Show at Pebble Beach Golf Links near Carmel, Calif., on Sunday. First American win since 2013.
Sandra Button, chairperson of the annual concours, said the car, whose chassis and body had been separated for years, "marries American force with European style." "Its resurrection story is passionate."

Pebble Beach Concours d'Elegance Auction
Since 1950, the Pebble Beach Concours d'Elegance has welcomed the world's most costly collectable vehicles for a week of parties, auctions, rallies, and high-roller meetings. The cold, dreary weather highlighted the automobiles' stunning lines and hues.
DPM/Bloomberg

A visitor photographs a 1948 Ferrari 166 MM Touring Barchetta. This is one of 25 Ferraris manufactured in the years after World War II. First shown at the 1948 Turin Salon. Others finished Mille Miglia and Le Mans, which set the tone for Ferrari racing for years.
DPM/Bloomberg
This year's frontrunners were ultra-rare pre-war and post-war automobiles with long and difficult titles, such a 1937 Talbot-Lago T150C-SS Figoni & Falaschi Teardrop Coupe and a 1951 Talbot-Lago T26 Grand Sport Stabilimenti Farina Cabriolet.
The hefty, enormous coaches inspire visions of golden pasts when mysterious saloons swept over the road with otherworldly style, speed, and grace. Only the richest and most powerful people, like Indian maharaja and Hollywood stars, owned such vehicles.
Antonio Chopitea, a Peruvian sugar tycoon, ordered a new Duesenberg in Paris. Hemmings says the two-tone blue beauty was moved to the US and dismantled in the 1960s. Body and chassis were sold separately and rejoined decades later in a three-year, prize-winning restoration.
The concours is the highlight of Monterey Car Week, a five-day Super Bowl for car enthusiasts. Early events included Porsche and Ferrari displays, antique automobile races, and new-vehicle debuts. Many auto executives call Monterey Car Week the "new auto show."
Many visitors were drawn to the record-breaking auctions.

A 1969 Porsche 908/02 auctioned for $4.185 million. Flat-eight air-cooled engine, 90.6-inch wheelbase, 1,320-pound weight. Vic Elford, Richard Attwood, Rudi Lins, Gérard Larrousse, Kurt Ahrens Jr., Masten Gregory, and Pedro Rodriguez drove it, according to Gooding.
DPM/Bloomberg

The 1931 Bentley Eight Liter Sports Tourer doesn't meet its reserve. Gooding & Co., the official auction house of the concours, made more than $105 million and had an 82% sell-through rate. This powerful open-top tourer is one of W.O. Bentley's 100 automobiles. Only 80 remain.
DPM/Bloomberg
The final auction on Aug. 21 brought in $456.1 million, breaking the previous high of $394.48 million established in 2015 in Monterey. “The week put an exclamation point on what has been an exceptional year for the collector automobile market,” Hagerty analyst John Wiley said.
Many cars that go unsold at public auction are sold privately in the days after. After-sales pushed the week's haul to $469 million on Aug. 22, up 18.9% from 2015's record.
In today's currencies, 2015's record sales amount to $490 million, Wiley noted. The dollar is degrading faster than old autos.
Still, 113 million-dollar automobiles sold. The average car sale price was $583,211, up from $446,042 last year, while multimillion-dollar hammer prices made up around 75% of total sales.
Industry insiders and market gurus expected that stock market volatility, the crisis in Ukraine, and the dollar-euro exchange rate wouldn't influence the world's biggest spenders.
Classic.com's CEO said there's no hint of a recession in an e-mail. Big sales and crowds.

Ticket-holders wore huge hats, flowery skirts, and other Kentucky Derby-esque attire. Coffee, beverages, and food are extra.
DPM/Bloomberg

Mercedes-Benz 300 SL Gullwing, 1955. Mercedes produced the two-seat gullwing coupe from 1954–1957 and the roadster from 1957–1963. It was once West Germany's fastest and most powerful automobile. You'd be hard-pressed to locate one for less $1 million.
DPM/Bloomberg
1955 Ferrari 410 Sport sold for $22 million at RM Sotheby's. It sold a 1937 Mercedes-Benz 540K Sindelfingen Roadster for $9.9 million and a 1924 Hispano-Suiza H6C Transformable Torpedo for $9.245 million. The family-run mansion sold $221.7 million with a 90% sell-through rate, up from $147 million in 2021. This year, RM Sotheby's cars averaged $1.3 million.
Not everyone saw such great benefits.
Gooding & Co., the official auction house of the concours, made more than $105 million and had an 82% sell-through rate. 1937 Bugatti Type 57SC Atalante, 1990 Ferrari F40, and 1994 Bugatti EB110 Super Sport were top sellers.

The 1969 Autobianchi A112 Bertone. This idea two-seater became a Hot Wheels toy but was never produced. It has a four-speed manual drive and an inline-four mid-engine arrangement like the Lamborghini Miura.
DPM/Bloomberg

1956 Porsche 356 A Speedster at Gooding & Co. The Porsche 356 is a lightweight, rear-engine, rear-wheel drive vehicle that lacks driving power but is loved for its rounded, Beetle-like hardtop coupé and open-top versions.
DPM/Bloomberg
Mecum sold $50.8 million with a 64% sell-through rate, down from $53.8 million and 77% in 2021. Its top lot, a 1958 Ferrari 250 GT 'Tour de France' Alloy Coupe, sold for $2.86 million, but its average price was $174,016.
Bonhams had $27.8 million in sales with an 88% sell-through rate. The same sell-through generated $35.9 million in 2021.
Gooding & Co. and RM Sotheby's posted all 10 top sales, leaving Bonhams, Mecum, and Hagerty-owned Broad Arrow fighting for leftovers. Six of the top 10 sellers were Ferraris, which remain the gold standard for collectable automobiles. Their prices have grown over decades.
Classic.com's Calle claimed RM Sotheby's "stole the show," but "BroadArrow will be a force to reckon with."
Although pre-war cars were hot, '80s and '90s cars showed the most appreciation and attention. Generational transition and new buyer profile."

2022 Pebble Beach Concours d'Elegance judges inspect 1953 Siata 208. The rounded coupe was introduced at the 1952 Turin Auto Show in Italy and is one of 18 ever produced. It sports a 120hp Fiat engine, five-speed manual transmission, and alloy drum brakes. Owners liked their style, but not their reliability.
DPM/Bloomberg

The Czinger 21 CV Max at Pebble Beach. Monterey Car Week concentrates on historic and classic automobiles, but modern versions like this Czinger hypercar also showed.
DPM/Bloomberg

The 1932 Duesenberg J Figoni Sports Torpedo won Best in Show in 2022. Lee and Penny Anderson of Naples, Fla., own the once-separate-chassis-from-body automobile.
DPM/Bloomberg

Bob Service
3 years ago
Did volcanic 'glasses' play a role in igniting early life?
Quenched lava may have aided in the formation of long RNA strands required by primitive life.
It took a long time for life to emerge. Microbes were present 3.7 billion years ago, just a few hundred million years after the 4.5-billion-year-old Earth had cooled enough to sustain biochemistry, according to fossils, and many scientists believe RNA was the genetic material for these first species. RNA, while not as complicated as DNA, would be difficult to forge into the lengthy strands required to transmit genetic information, raising the question of how it may have originated spontaneously.
Researchers may now have a solution. They demonstrate how basaltic glasses assist individual RNA letters, also known as nucleoside triphosphates, join into strands up to 200 letters long in lab studies. The glasses are formed when lava is quenched in air or water, or when melted rock generated by asteroid strikes cools rapidly, and they would have been plentiful in the early Earth's fire and brimstone.
The outcome has caused a schism among top origin-of-life scholars. "This appears to be a great story that finally explains how nucleoside triphosphates react with each other to create RNA strands," says Thomas Carell, a scientist at Munich's Ludwig Maximilians University. However, Harvard University's Jack Szostak, an RNA expert, says he won't believe the results until the study team thoroughly describes the RNA strands.
Researchers interested in the origins of life like the idea of a primordial "RNA universe" since the molecule can perform two different functions that are essential for life. It's made up of four chemical letters, just like DNA, and can carry genetic information. RNA, like proteins, can catalyze chemical reactions that are necessary for life.
However, RNA can cause headaches. No one has yet discovered a set of plausible primordial conditions that would cause hundreds of RNA letters—each of which is a complicated molecule—to join together into strands long enough to support the intricate chemistry required to kick-start evolution.
Basaltic glasses may have played a role, according to Stephen Mojzsis, a geologist at the University of Colorado, Boulder. They're high in metals like magnesium and iron, which help to trigger a variety of chemical reactions. "Basaltic glass was omnipresent on Earth at the time," he adds.
He provided the Foundation for Applied Molecular Evolution samples of five different basalt glasses. Each sample was ground into a fine powder, sanitized, and combined with a solution of nucleoside triphosphates by molecular biologist Elisa Biondi and her colleagues. The RNA letters were unable to link up without the presence of glass powder. However, when the molecules were mixed with the glass particles, they formed long strands of hundreds of letters, according to the researchers, who published their findings in Astrobiology this week. There was no need for heat or light. Biondi explains, "All we had to do was wait." After only a day, little RNA strands produced, yet the strands continued to grow for months. Jan Paek, a molecular biologist at Firebird Biomolecular Sciences, says, "The beauty of this approach is its simplicity." "Mix the components together, wait a few days, and look for RNA."
Nonetheless, the findings pose a slew of problems. One of the questions is how nucleoside triphosphates came to be in the first place. Recent study by Biondi's colleague Steven Benner suggests that the same basaltic glasses may have aided in the creation and stabilization of individual RNA letters.
The form of the lengthy RNA strands, according to Szostak, is a significant challenge. Enzymes in modern cells ensure that most RNAs form long linear chains. RNA letters, on the other hand, can bind in complicated branching sequences. Szostak wants the researchers to reveal what kind of RNA was produced by the basaltic glasses. "It irritates me that the authors made an intriguing initial finding but then chose to follow the hype rather than the research," Szostak says.
Biondi acknowledges that her team's experiment almost probably results in some RNA branching. She does acknowledge, however, that some branched RNAs are seen in species today, and that analogous structures may have existed before the origin of life. Other studies carried out by the study also confirmed the presence of lengthy strands with connections, indicating that they are most likely linear. "It's a healthy argument," says Dieter Braun, a Ludwig Maximilian University origin-of-life chemist. "It will set off the next series of tests."
