5 Bored Apes borrowed to claim $1.1 million in APE tokens
Takeaway
Unknown user took advantage of the ApeCoin airdrop to earn $1.1 million.
He used a flash loan to borrow five BAYC NFTs, claim the airdrop, and repay the NFTs.
Yuga Labs, the creators of BAYC, airdropped ApeCoin (APE) to anyone who owns one of their NFTs yesterday.
For the Bored Ape Yacht Club and Mutant Ape Yacht Club collections, the team allocated 150 million tokens, or 15% of the total ApeCoin supply, worth over $800 million. Each BAYC holder received 10,094 tokens worth $80,000 to $200,000.
But someone managed to claim the airdrop using NFTs they didn't own. They used the airdrop's specific features to carry it out. And it worked, earning them $1.1 million in ApeCoin.
The trick was that the ApeCoin airdrop wasn't based on who owned which Bored Ape at a given time. Instead, anyone with a Bored Ape at the time of the airdrop could claim it. So if you gave someone your Bored Ape and you hadn't claimed your tokens, they could claim them.
The person only needed to get hold of some Bored Apes that hadn't had their tokens claimed to claim the airdrop. They could be returned immediately.
So, what happened?
The person found a vault with five Bored Ape NFTs that hadn't been used to claim the airdrop.
A vault tokenizes an NFT or a group of NFTs. You put a bunch of NFTs in a vault and make a token. This token can then be staked for rewards or sold (representing part of the value of the collection of NFTs). Anyone with enough tokens can exchange them for NFTs.
This vault uses the NFTX protocol. In total, it contained five Bored Apes: #7594, #8214, #9915, #8167, and #4755. Nobody had claimed the airdrop because the NFTs were locked up in the vault and not controlled by anyone.
The person wanted to unlock the NFTs to claim the airdrop but didn't want to buy them outright s o they used a flash loan, a common tool for large DeFi hacks. Flash loans are a low-cost way to borrow large amounts of crypto that are repaid in the same transaction and block (meaning that the funds are never at risk of not being repaid).
With a flash loan of under $300,000 they bought a Bored Ape on NFT marketplace OpenSea. A large amount of the vault's token was then purchased, allowing them to redeem the five NFTs. The NFTs were used to claim the airdrop, before being returned, the tokens sold back, and the loan repaid.
During this process, they claimed 60,564 ApeCoin airdrops. They then sold them on Uniswap for 399 ETH ($1.1 million). Then they returned the Bored Ape NFT used as collateral to the same NFTX vault.
Attack or arbitrage?
However, security firm BlockSecTeam disagreed with many social media commentators. A flaw in the airdrop-claiming mechanism was exploited, it said.
According to BlockSecTeam's analysis, the user took advantage of a "vulnerability" in the airdrop.
"We suspect a hack due to a flaw in the airdrop mechanism. The attacker exploited this vulnerability to profit from the airdrop claim" said BlockSecTeam.
For example, the airdrop could have taken into account how long a person owned the NFT before claiming the reward.
Because Yuga Labs didn't take a snapshot, anyone could buy the NFT in real time and claim it. This is probably why BAYC sales exploded so soon after the airdrop announcement.
More on NFTs & Art

middlemarch.eth
3 years ago
ERC721R: A new ERC721 contract for random minting so people don’t snipe all the rares!
That is, how to snipe all the rares without using ERC721R!
Introduction: Blessed and Lucky
Mphers was the first mfers derivative, and as a Phunks derivative, I wanted one.
I wanted an alien. And there are only 8 in the 6,969 collection. I got one!
In case it wasn't clear from the tweet, I meant that I was lucky to have figured out how to 100% guarantee I'd get an alien without any extra luck.
Read on to find out how I did it, how you can too, and how developers can avoid it!
How to make rare NFTs without luck.
# How to mint rare NFTs without needing luck
The key to minting a rare NFT is knowing the token's id ahead of time.
For example, once I knew my alien was #4002, I simply refreshed the mint page until #3992 was minted, and then mint 10 mphers.
How did I know #4002 was extraterrestrial? Let's go back.
First, go to the mpher contract's Etherscan page and look up the tokenURI of a previously issued token, token #1:
As you can see, mphers creates metadata URIs by combining the token id and an IPFS hash.
This method gives you the collection's provenance in every URI, and while that URI can be changed, it affects everyone and is public.
Consider a token URI without a provenance hash, like https://mphers.art/api?tokenId=1.
As a collector, you couldn't be sure the devs weren't changing #1's metadata at will.
The API allows you to specify “if #4002 has not been minted, do not show any information about it”, whereas IPFS does not allow this.
It's possible to look up the metadata of any token, whether or not it's been minted.
Simply replace the trailing “1” with your desired id.
Mpher #4002
These files contain all the information about the mpher with the specified id. For my alien, we simply search all metadata files for the string “alien mpher.”
Take a look at the 6,969 meta-data files I'm using OpenSea's IPFS gateway, but you could use ipfs.io or something else.
Use curl to download ten files at once. Downloading thousands of files quickly can lead to duplicates or errors. But with a little tweaking, you should be able to get everything (and dupes are fine for our purposes).
Now that you have everything in one place, grep for aliens:
The numbers are the file names that contain “alien mpher” and thus the aliens' ids.
The entire process takes under ten minutes. This technique works on many NFTs currently minting.
In practice, manually minting at the right time to get the alien is difficult, especially when tokens mint quickly. Then write a bot to poll totalSupply() every second and submit the mint transaction at the exact right time.
You could even look for the token you need in the mempool before it is minted, and get your mint into the same block!
However, in my experience, the “big” approach wins 95% of the time—but not 100%.
“Am I being set up all along?”
Is a question you might ask yourself if you're new to this.
It's disheartening to think you had no chance of minting anything that someone else wanted.
But, did you have no opportunity? You had an equal chance as everyone else!
Take me, for instance: I figured this out using open-source tools and free public information. Anyone can do this, and not understanding how a contract works before minting will lead to much worse issues.
The mpher mint was fair.
While a fair game, “snipe the alien” may not have been everyone's cup of tea.
People may have had more fun playing the “mint lottery” where tokens were distributed at random and no one could gain an advantage over someone simply clicking the “mint” button.
How might we proceed?
Minting For Fashion Hats Punks, I wanted to create a random minting experience without sacrificing fairness. In my opinion, a predictable mint beats an unfair one. Above all, participants must be equal.
Sadly, the most common method of creating a random experience—the post-mint “reveal”—is deeply unfair. It works as follows:
- During the mint, token metadata is unavailable. Instead, tokenURI() returns a blank JSON file for each id.
- An IPFS hash is updated once all tokens are minted.
- You can't tell how the contract owner chose which token ids got which metadata, so it appears random.
Because they alone decide who gets what, the person setting the metadata clearly has a huge unfair advantage over the people minting. Unlike the mpher mint, you have no chance of winning here.
But what if it's a well-known, trusted, doxxed dev team? Are reveals okay here?
No! No one should be trusted with such power. Even if someone isn't consciously trying to cheat, they have unconscious biases. They might also make a mistake and not realize it until it's too late, for example.
You should also not trust yourself. Imagine doing a reveal, thinking you did it correctly (nothing is 100%! ), and getting the rarest NFT. Isn't that a tad odd Do you think you deserve it? An NFT developer like myself would hate to be in this situation.
Reveals are bad*
UNLESS they are done without trust, meaning everyone can verify their fairness without relying on the developers (which you should never do).
An on-chain reveal powered by randomness that is verifiably outside of anyone's control is the most common way to achieve a trustless reveal (e.g., through Chainlink).
Tubby Cats did an excellent job on this reveal, and I highly recommend their contract and launch reflections. Their reveal was also cool because it was progressive—you didn't have to wait until the end of the mint to find out.
In his post-launch reflections, @DefiLlama stated that he made the contract as trustless as possible, removing as much trust as possible from the team.
In my opinion, everyone should know the rules of the game and trust that they will not be changed mid-stream, while trust minimization is critical because smart contracts were designed to reduce trust (and it makes it impossible to hack even if the team is compromised). This was a huge mistake because it limited our flexibility and our ability to correct mistakes.
And @DefiLlama is a superstar developer. Imagine how much stress maximizing trustlessness will cause you!
That leaves me with a bad solution that works in 99 percent of cases and is much easier to implement: random token assignments.
Introducing ERC721R: A fully compliant IERC721 implementation that picks token ids at random.
ERC721R implements the opposite of a reveal: we mint token ids randomly and assign metadata deterministically.
This allows us to reveal all metadata prior to minting while reducing snipe chances.
Then import the contract and use this code:
What is ERC721R and how does it work
First, a disclaimer: ERC721R isn't truly random. In this sense, it creates the same “game” as the mpher situation, where minters compete to exploit the mint. However, ERC721R is a much more difficult game.
To game ERC721R, you need to be able to predict a hash value using these inputs:
This is impossible for a normal person because it requires knowledge of the block timestamp of your mint, which you do not have.
To do this, a miner must set the timestamp to a value in the future, and whatever they do is dependent on the previous block's hash, which expires in about ten seconds when the next block is mined.
This pseudo-randomness is “good enough,” but if big money is involved, it will be gamed. Of course, the system it replaces—predictable minting—can be manipulated.
The token id is chosen in a clever implementation of the Fisher–Yates shuffle algorithm that I copied from CryptoPhunksV2.
Consider first the naive solution: (a 10,000 item collection is assumed):
- Make an array with 0–9999.
- To create a token, pick a random item from the array and use that as the token's id.
- Remove that value from the array and shorten it by one so that every index corresponds to an available token id.
This works, but it uses too much gas because changing an array's length and storing a large array of non-zero values is expensive.
How do we avoid them both? What if we started with a cheap 10,000-zero array? Let's assign an id to each index in that array.
Assume we pick index #6500 at random—#6500 is our token id, and we replace the 0 with a 1.
But what if we chose #6500 again? A 1 would indicate #6500 was taken, but then what? We can't just "roll again" because gas will be unpredictable and high, especially later mints.
This allows us to pick a token id 100% of the time without having to keep a separate list. Here's how it works:
- Make a 10,000 0 array.
- Create a 10,000 uint numAvailableTokens.
- Pick a number between 0 and numAvailableTokens. -1
- Think of #6500—look at index #6500. If it's 0, the next token id is #6500. If not, the value at index #6500 is your next token id (weird!)
- Examine the array's last value, numAvailableTokens — 1. If it's 0, move the value at #6500 to the end of the array (#9999 if it's the first token). If the array's last value is not zero, update index #6500 to store it.
- numAvailableTokens is decreased by 1.
- Repeat 3–6 for the next token id.
So there you go! The array stays the same size, but we can choose an available id reliably. The Solidity code is as follows:
Unfortunately, this algorithm uses more gas than the leading sequential mint solution, ERC721A.
This is most noticeable when minting multiple tokens in one transaction—a 10 token mint on ERC721R costs 5x more than on ERC721A. That said, ERC721A has been optimized much further than ERC721R so there is probably room for improvement.
Conclusion
Listed below are your options:
- ERC721A: Minters pay lower gas but must spend time and energy devising and executing a competitive minting strategy or be comfortable with worse minting results.
- ERC721R: Higher gas, but the easy minting strategy of just clicking the button is optimal in all but the most extreme cases. If miners game ERC721R it’s the worst of both worlds: higher gas and a ton of work to compete.
- ERC721A + standard reveal: Low gas, but not verifiably fair. Please do not do this!
- ERC721A + trustless reveal: The best solution if done correctly, highly-challenging for dev, potential for difficult-to-correct errors.
Did I miss something? Comment or tweet me @dumbnamenumbers.
Check out the code on GitHub to learn more! Pull requests are welcome—I'm sure I've missed many gas-saving opportunities.
Thanks!
Read the original post here

Jake Prins
3 years ago
What are NFTs 2.0 and what issues are they meant to address?
New standards help NFTs reach their full potential.

NFTs lack interoperability and functionality. They have great potential but are mostly speculative. To maximize NFTs, we need flexible smart contracts.
Current requirements are too restrictive.
Most NFTs are based on ERC-721, which makes exchanging them easy. CryptoKitties, a popular online game, used the 2017 standard to demonstrate NFTs' potential.
This simple standard includes a base URI and incremental IDs for tokens. Add the tokenID to the base URI to get the token's metadata.
This let creators collect NFTs. Many NFT projects store metadata on IPFS, a distributed storage network, but others use Google Drive. NFT buyers often don't realize that if the creators delete or move the files, their NFT is just a pointer.
This isn't the standard's biggest issue. There's no way to validate NFT projects.
Creators are one of the most important aspects of art, but nothing is stored on-chain.
ERC-721 contracts only have a name and symbol.
Most of the data on OpenSea's collection pages isn't from the NFT's smart contract. It was added through a platform input field, so it's in the marketplace's database. Other websites may have different NFT information.
In five years, your NFT will be just a name, symbol, and ID.
Your NFT doesn't mention its creators. Although the smart contract has a public key, it doesn't reveal who created it.
The NFT's creators and their reputation are crucial to its value. Think digital fashion and big brands working with well-known designers when more professionals use NFTs. Don't you want them in your NFT?
Would paintings be as valuable if their artists were unknown? Would you believe it's real?
Buying directly from an on-chain artist would reduce scams. Current standards don't allow this data.
Most creator profiles live on centralized marketplaces and could disappear. Current platforms have outpaced underlying standards. The industry's standards are lagging.
For NFTs to grow beyond pointers to a monkey picture file, we may need to use new Web3-based standards.
Introducing NFTs 2.0
Fabian Vogelsteller, creator of ERC-20, developed new web3 standards. He proposed LSP7 Digital Asset and LSP8 Identifiable Digital Asset, also called NFT 2.0.
NFT and token metadata inputs are extendable. Changes to on-chain metadata inputs allow NFTs to evolve. Instead of public keys, the contract can have Universal Profile addresses attached. These profiles show creators' faces and reputations. NFTs can notify asset receivers, automating smart contracts.
LSP7 and LSP8 use ERC725Y. Using a generic data key-value store gives contracts much-needed features:
The asset can be customized and made to stand out more by allowing for unlimited data attachment.
Recognizing changes to the metadata
using a hash reference for metadata rather than a URL reference
This base will allow more metadata customization and upgradeability. These guidelines are:
Genuine and Verifiable Now, the creation of an NFT by a specific Universal Profile can be confirmed by smart contracts.
Dynamic NFTs can update Flexible & Updatable Metadata, allowing certain things to evolve over time.
Protected metadata Now, secure metadata that is readable by smart contracts can be added indefinitely.
Better NFTS prevent the locking of NFTs by only being sent to Universal Profiles or a smart contract that can interact with them.
Summary
NFTS standards lack standardization and powering features, limiting the industry.
ERC-721 is the most popular NFT standard, but it only represents incremental tokenIDs without metadata or asset representation. No standard sender-receiver interaction or security measures ensure safe asset transfers.
NFT 2.0 refers to the new LSP7-DigitalAsset and LSP8-IdentifiableDigitalAsset standards.
They have new standards for flexible metadata, secure transfers, asset representation, and interactive transfer.
With NFTs 2.0 and Universal Profiles, creators could build on-chain reputations.
NFTs 2.0 could bring the industry's needed innovation if it wants to move beyond trading profile pictures for speculation.

Stephen Moore
3 years ago
Trading Volume on OpenSea Drops by 99% as the NFT Boom Comes to an End
Wasn't that a get-rich-quick scheme?

OpenSea processed $2.7 billion in NFT transactions in May 2021.
Fueled by a crypto bull run, rumors of unfathomable riches, and FOMO, Bored Apes, Crypto Punks, and other JPEG-format trash projects flew off the virtual shelves, snatched up by retail investors and celebrities alike.
Over a year later, those shelves are overflowing and warehouses are backlogged. Since March, I've been writing less. In May and June, the bubble was close to bursting.
Apparently, the boom has finally peaked.
This bubble has punctured, and deflation has begun. On Aug. 28, OpenSea processed $9.34 million.
From that euphoric high of $2.7 billion, $9.34 million represents a spectacular decline of 99%.
OpenSea contradicts the data. A trading platform spokeswoman stated the comparison is unfair because it compares the site's highest and lowest trading days. They're the perfect two data points to assess the drop. OpenSea chooses to use ETH volume measures, which ignore crypto's shifting price. Since January 2022, monthly ETH volume has dropped 140%, according to Dune.
Unconvincing counterargument.
Further OpenSea indicators point to declining NFT demand:
Since January 2022, daily user visits have decreased by 50%.
Daily transactions have decreased by 50% since the beginning of the year in the same manner.
Off-platform, the floor price of Bored Apes has dropped from 145 ETH to 77 ETH. (At $4,800, a reduction from $700,000 to $370,000). Google search data shows waning popular interest.

It is a trend that will soon vanish, just like laser eyes.
NFTs haven't moved since the new year. Eminem and Snoop Dogg can utilize their apes in music videos or as 3D visuals to perform at the VMAs, but the reality is that NFTs have lost their public appeal and the market is trying to regain its footing.
They've lost popularity because?
Breaking records. The technology still lacks genuine use cases a year and a half after being popular.
They're pricey prestige symbols that have made a few people rich through cunning timing or less-than-savory scams or rug pulling. Over $10.5 billion has been taken through frauds, most of which are NFT enterprises promising to be the next Bored Apes, according to Web3 is going wonderfully. As the market falls, many ordinary investors realize they purchased into a self-fulfilling ecosystem that's halted. Many NFTs are sold between owner-held accounts to boost their price, data suggests. Most projects rely on social media excitement to debut with a high price before the first owners sell and chuckle to the bank. When they don't, the initiative fails, leaving investors high and dry.
NFTs are fading like laser eyes. Most people pushing the technology don't believe in it or the future it may bring. No, they just need a Kool-Aid-drunk buyer.
Everybody wins. When your JPEGs are worth 99% less than when you bought them, you've lost.
When demand reaches zero, many will lose.
You might also like

Jano le Roux
3 years ago
Here's What I Learned After 30 Days Analyzing Apple's Microcopy
Move people with tiny words.

Apple fanboy here.
Macs are awesome.
Their iPhones rock.
$19 cloths are great.
$999 stands are amazing.
I love Apple's microcopy even more.
It's like the marketing goddess bit into the Apple logo and blessed the world with microcopy.
I took on a 30-day micro-stalking mission.
Every time I caught myself wasting time on YouTube, I had to visit Apple’s website to learn the secrets of the marketing goddess herself.
We've learned. Golden apples are calling.
Cut the friction
Benefit-first, not commitment-first.
Brands lose customers through friction.
Most brands don't think like customers.
Brands want sales.
Brands want newsletter signups.
Here's their microcopy:
“Buy it now.”
“Sign up for our newsletter.”
Both are difficult. They ask for big commitments.
People are simple creatures. Want pleasure without commitment.
Apple nails this.
So, instead of highlighting the commitment, they highlight the benefit of the commitment.
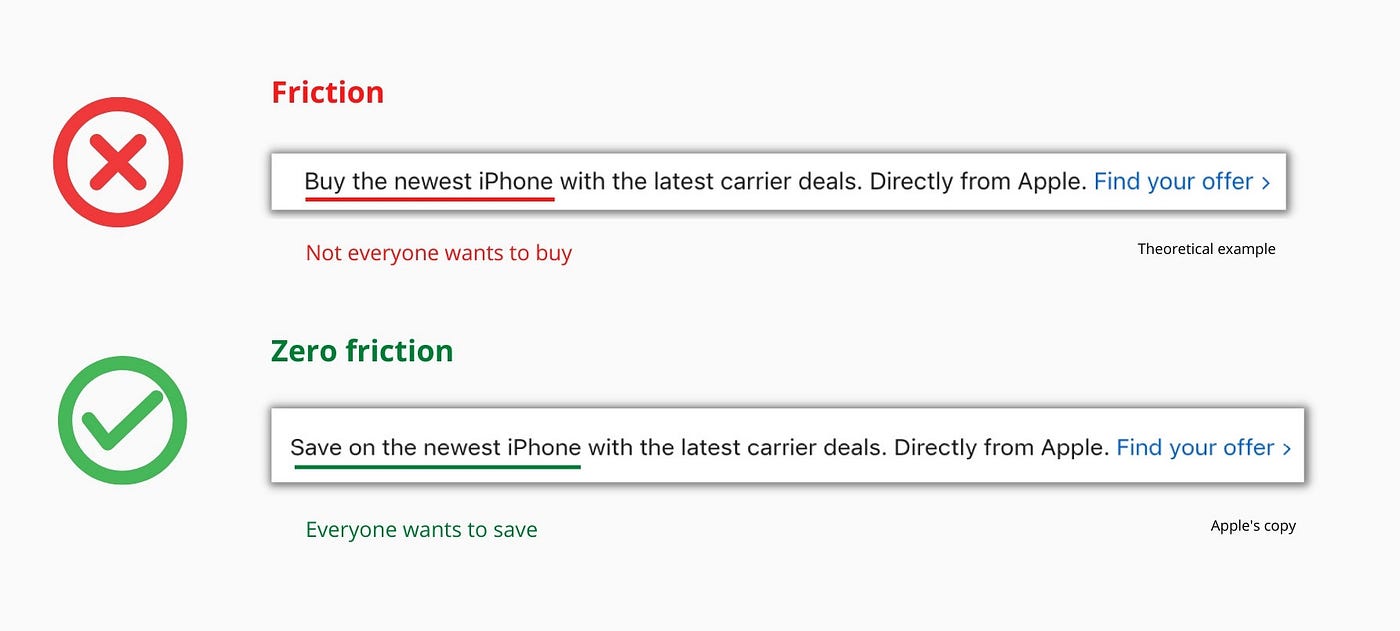
Saving on the latest iPhone sounds easier than buying it. Everyone saves, but not everyone buys.
A subtle change in framing reduces friction.
Apple eliminates customer objections to reduce friction.
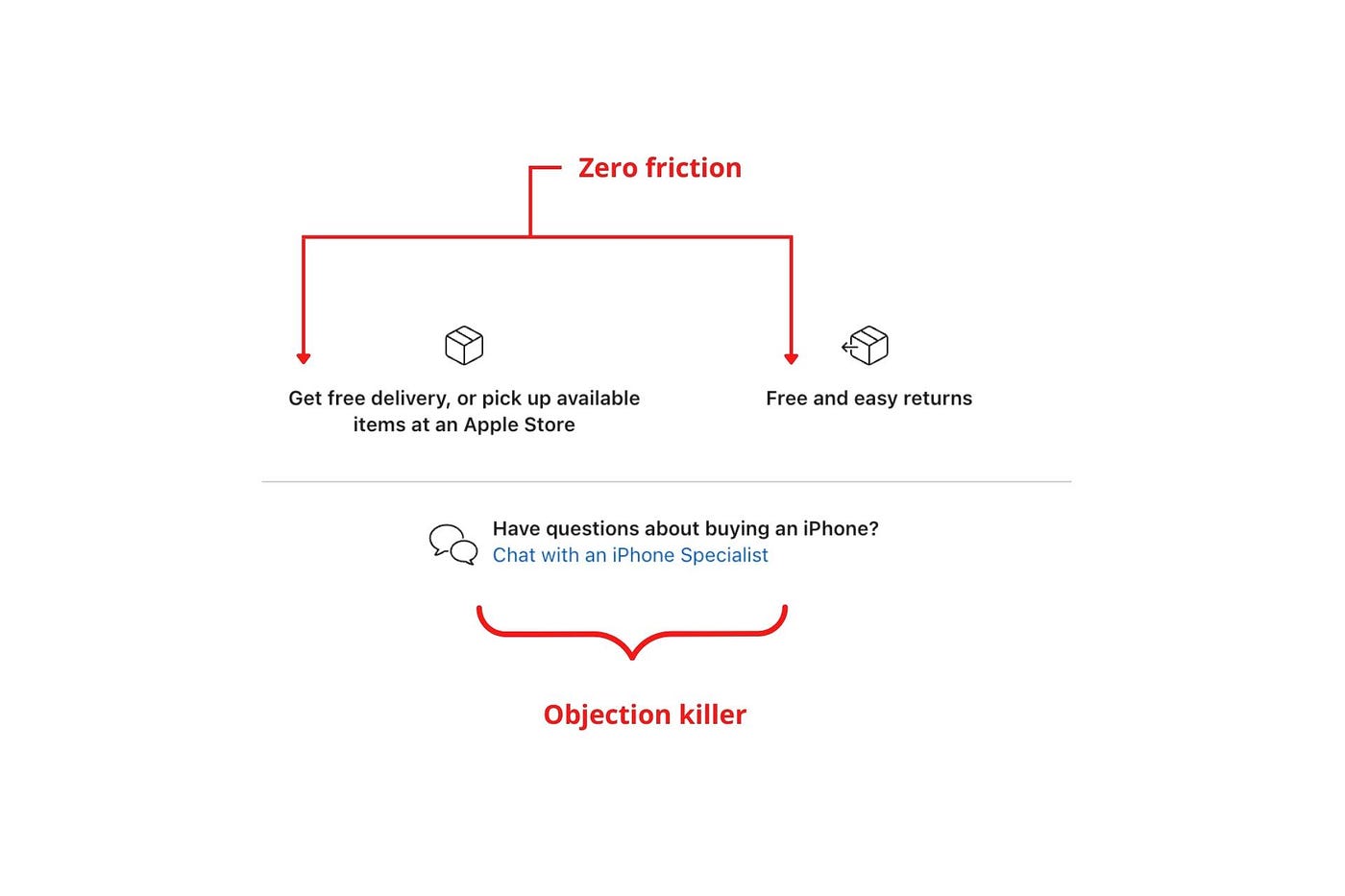
Less customer friction means simpler processes.
Apple's copy expertly reassures customers about shipping fees and not being home. Apple assures customers that returning faulty products is easy.
Apple knows that talking to a real person is the best way to reduce friction and improve their copy.
Always rhyme
Learn about fine rhyme.
Poets make things beautiful with rhyme.
Copywriters use rhyme to stand out.
Apple’s copywriters have mastered the art of corporate rhyme.
Two techniques are used.
1. Perfect rhyme
Here, rhymes are identical.

2. Imperfect rhyme
Here, rhyming sounds vary.

Apple prioritizes meaning over rhyme.
Apple never forces rhymes that don't fit.
It fits so well that the copy seems accidental.
Add alliteration
Alliteration always entertains.
Alliteration repeats initial sounds in nearby words.
Apple's copy uses alliteration like no other brand I've seen to create a rhyming effect or make the text more fun to read.
For example, in the sentence "Sam saw seven swans swimming," the initial "s" sound is repeated five times. This creates a pleasing rhythm.
Microcopy overuse is like pouring ketchup on a Michelin-star meal.
Alliteration creates a memorable phrase in copywriting. It's subtler than rhyme, and most people wouldn't notice; it simply resonates.

I love how Apple uses alliteration and contrast between "wonders" and "ease".
Assonance, or repeating vowels, isn't Apple's thing.
You ≠ Hero, Customer = Hero
Your brand shouldn't be the hero.
Because they'll be using your product or service, your customer should be the hero of your copywriting. With your help, they should feel like they can achieve their goals.
I love how Apple emphasizes what you can do with the machine in this microcopy.

It's divine how they position their tools as sidekicks to help below.

This one takes the cake:

Dialogue-style writing
Conversational copy engages.
Excellent copy Like sharing gum with a friend.
This helps build audience trust.

Apple does this by using natural connecting words like "so" and phrases like "But that's not all."
Snowclone-proof
The mother of all microcopy techniques.
A snowclone uses an existing phrase or sentence to create a new one. The new phrase or sentence uses the same structure but different words.
It’s usually a well know saying like:
To be or not to be.
This becomes a formula:
To _ or not to _.
Copywriters fill in the blanks with cause-related words. Example:
To click or not to click.

Apple turns "survival of the fittest" into "arrival of the fittest."
It's unexpected and surprises the reader.
So this was fun.
But my fun has just begun.
Microcopy is 21st-century poetry.
I came as an Apple fanboy.
I leave as an Apple fanatic.
Now I’m off to find an apple tree.
Cause you know how it goes.
(Apples, trees, etc.)
This post is a summary. Original post available here.
Sam Hickmann
3 years ago
Token taxonomy: Utility vs Security vs NFT
Let's examine the differences between the three main token types and their functions.
As Ethereum grew, the term "token" became a catch-all term for all assets built on the Ethereum blockchain. However, different tokens were grouped based on their applications and features, causing some confusion. Let's examine the modification of three main token types: security, utility, and non-fungible.
Utility tokens
They provide a specific utility benefit (or a number of such). A utility token is similar to a casino chip, a table game ticket, or a voucher. Depending on the terms of issuing, they can be earned and used in various ways. A utility token is a type of token that represents a tool or mechanism required to use the application in question. Like a service, a utility token's price is determined by supply and demand. Tokens can also be used as a bonus or reward mechanism in decentralized systems: for example, if you like someone's work, give them an upvote and they get a certain number of tokens. This is a way for authors or creators to earn money indirectly.
The most common way to use a utility token is to pay with them instead of cash for discounted goods or services.
Utility tokens are the most widely used by blockchain companies. Most cryptocurrency exchanges accept fees in native utility tokens.
Utility tokens can also be used as a reward. Companies tokenize their loyalty programs so that points can be bought and sold on blockchain exchanges. These tokens are widely used in decentralized companies as a bonus system. You can use utility tokens to reward creators for their contributions to a platform, for example. It also allows members to exchange tokens for specific bonuses and rewards on your site.
Unlike security tokens, which are subject to legal restrictions, utility tokens can be freely traded.
Security tokens
Security tokens are essentially traditional securities like shares, bonds, and investment fund units in a crypto token form.
The key distinction is that security tokens are typically issued by private firms (rather than public companies) that are not listed on stock exchanges and in which you can not invest right now. Banks and large venture funds used to be the only sources of funding. A person could only invest in private firms if they had millions of dollars in their bank account. Privately issued security tokens outperform traditional public stocks in terms of yield. Private markets grew 50% faster than public markets over the last decade, according to McKinsey Private Equity Research.
A security token is a crypto token whose value is derived from an external asset or company. So it is governed as security (read about the Howey test further in this article). That is, an ownership token derives its value from the company's valuation, assets on the balance sheet, or dividends paid to token holders.
Why are Security Tokens Important?
Cryptocurrency is a lucrative investment. Choosing from thousands of crypto assets can mean the difference between millionaire and bankrupt. Without security tokens, crypto investing becomes riskier and generating long-term profits becomes difficult. These tokens have lower risk than other cryptocurrencies because they are backed by real assets or business cash flows. So having them helps to diversify a portfolio and preserve the return on investment in riskier assets.
Security tokens open up new funding avenues for businesses. As a result, investors can invest in high-profit businesses that are not listed on the stock exchange.
The distinction between utility and security tokens isn't as clear as it seems. However, this increases the risk for token issuers, especially in the USA. The Howey test is the main pillar regulating judicial precedent in this area.
What is a Howey Test?
An "investment contract" is determined by the Howey Test, a lawsuit settled by the US Supreme Court. If it does, it's a security and must be disclosed and registered under the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
If the SEC decides that a cryptocurrency token is a security, a slew of issues arise. In practice, this ensures that the SEC will decide when a token can be offered to US investors and if the project is required to file a registration statement with the SEC.
Due to the Howey test's extensive wording, most utility tokens will be classified as securities, even if not intended to be. Because of these restrictions, most ICOs are not available to US investors. When asked about ICOs in 2018, then-SEC Chairman Jay Clayton said they were securities. The given statement adds to the risk. If a company issues utility tokens without registering them as securities, the regulator may impose huge fines or even criminal charges.
What other documents regulate tokens?
Securities Act (1993) or Securities Exchange Act (1934) in the USA; MiFID directive and Prospectus Regulation in the EU. These laws require registering the placement of security tokens, limiting their transfer, but protecting investors.
Utility tokens have much less regulation. The Howey test determines whether a given utility token is a security. Tokens recognized as securities are now regulated as such. Having a legal opinion that your token isn't makes the implementation process much easier. Most countries don't have strict regulations regarding utility tokens except KYC (Know Your Client) and AML (Anti Money-Laundering).
As cryptocurrency and blockchain technologies evolve, more countries create UT regulations. If your company is based in the US, be aware of the Howey test and the Bank Secrecy Act. It classifies UTs and their issuance as money transmission services in most states, necessitating a license and strict regulations. Due to high regulatory demands, UT issuers try to avoid the United States as a whole. A new law separating utility tokens from bank secrecy act will be introduced in the near future, giving hope to American issuers.
The rest of the world has much simpler rules requiring issuers to create basic investor disclosures. For example, the latest European legislation (MiCA) allows businesses to issue utility tokens without regulator approval. They must also prepare a paper with all the necessary information for the investors.
A payment token is a utility token that is used to make a payment. They may be subject to electronic money laws.
Because non-fungible tokens are a new instrument, there is no regulating paper yet. However, if the NFT is fractionalized, the smaller tokens acquired may be seen as securities.
NFT Tokens
Collectible tokens are also known as non-fungible tokens. Their distinctive feature is that they denote unique items such as artwork, merch, or ranks. Unlike utility tokens, which are fungible, meaning that two of the same tokens are identical, NFTs represent a unit of possession that is strictly one of a kind. In a way, NFTs are like baseball cards, each one unique and valuable.
As for today, the most recognizable NFT function is to preserve the fact of possession. Owning an NFT with a particular gif, meme, or sketch does not transfer the intellectual right to the possessor, but is analogous to owning an original painting signed by the author.
Collectible tokens can also be used as digital souvenirs, so to say. Businesses can improve their brand image by issuing their own branded NFTs, which represent ranks or achievements within the corporate ecosystem. Gamifying business ecosystems would allow people to connect with a brand and feel part of a community.
Which type of tokens is right for you as a business to raise capital?
For most businesses, it's best to raise capital with security tokens by selling existing shares to global investors. Utility tokens aren't meant to increase in value over time, so leave them for gamification and community engagement. In a blockchain-based business, however, a utility token is often the lifeblood of the operation, and its appreciation potential is directly linked to the company's growth. You can issue multiple tokens at once, rather than just one type. It exposes you to various investors and maximizes the use of digital assets.
Which tokens should I buy?
There are no universally best tokens. Their volatility, industry, and risk-reward profile vary. This means evaluating tokens in relation to your overall portfolio and personal preferences: what industries do you understand best, what excites you, how do you approach taxes, and what is your planning horizon? To build a balanced portfolio, you need to know these factors.
Conclusion
The three most common types of tokens today are security, utility, and NFT. Security tokens represent stocks, mutual funds, and bonds. Utility tokens can be perceived as an inside-product "currency" or "ignition key" that grants you access to goods and services or empowers with other perks. NFTs are unique collectible units that identify you as the owner of something.

Christian Soschner
3 years ago
Steve Jobs' Secrets Revealed
From 1984 until 2011, he ran Apple using the same template.

What is a founder CEO's most crucial skill?
Presentation, communication, and sales
As a Business Angel Investor, I saw many pitch presentations and met with investors one-on-one to promote my companies.
There is always the conception of “Investors have to invest,” so there is no need to care about the presentation.
It's false. Nobody must invest. Many investors believe that entrepreneurs must convince them to invest in their business.
Sometimes — like in 2018–2022 — too much money enters the market, and everyone makes good money.
Do you recall the Buy Now, Pay Later Movement? This amazing narrative had no return potential. Only buyers who couldn't acquire financing elsewhere shopped at these companies.
Klarna's failing business concept led to high valuations.
Investors become more cautious when the economy falters. 2022 sees rising inflation, interest rates, wars, and civil instability. It's like the apocalypse's four horsemen have arrived.
Storytelling is important in rough economies.
When investors draw back, how can entrepreneurs stand out?
In Q2/2022, every study I've read said:
Investors cease investing
Deals are down in almost all IT industries from previous quarters.
What do founders need to do?
Differentiate yourself.
Storytelling talents help.
The Steve Jobs Way
Every time I watch a Steve Jobs presentation, I'm enthralled.
I'm a techie. Everything technical interests me. But, I skim most presentations.
What's Steve Jobs's secret?
Steve Jobs created Apple in 1976 and made it a profitable software and hardware firm in the 1980s. Macintosh goods couldn't beat IBM's. This mistake sacked him in 1985.
Before rejoining Apple in 1997, Steve Jobs founded Next Inc. and Pixar.
From then on, Apple became America's most valuable firm.
Steve Jobs understood people's needs. He said:
“People don’t know what they want until you show it to them. That’s why I never rely on market research. Our task is to read things that are not yet on the page.”
In his opinion, people talk about problems. A lot. Entrepreneurs must learn what the population's pressing problems are and create a solution.
Steve Jobs showed people what they needed before they realized it.
I'll explain:
Present a Big Vision
Steve Jobs starts every presentation by describing his long-term goals for Apple.
1984's Macintosh presentation set up David vs. Goliath. In a George Orwell-style dystopia, IBM computers were bad. It was 1984.
Apple will save the world, like Jedis.
Why do customers and investors like Big Vision?
People want a wider perspective, I think. Humans love improving the planet.
Apple users often cite emotional reasons for buying the brand.
Revolutionizing several industries with breakthrough inventions
Establish Authority
Everyone knows Apple in 2022. It's hard to find folks who confuse Apple with an apple around the world.
Apple wasn't as famous as it is today until Steve Jobs left in 2011.
Most entrepreneurs lack experience. They may market their company or items to folks who haven't heard of it.
Steve Jobs presented the company's historical accomplishments to overcome opposition.
In his presentation of the first iPhone, he talked about the Apple Macintosh, which altered the computing sector, and the iPod, which changed the music industry.
People who have never heard of Apple feel like they're seeing a winner. It raises expectations that the new product will be game-changing and must-have.
The Big Reveal
A pitch or product presentation always has something new.
Steve Jobs doesn't only demonstrate the product. I don't think he'd skip the major point of a company presentation.
He consistently discusses present market solutions, their faults, and a better consumer solution.
No solution exists yet.
It's a multi-faceted play:
It's comparing the new product to something familiar. This makes novelty and the product more relatable.
Describe a desirable solution.
He's funny. He demonstrated an iPod with an 80s phone dial in his iPhone presentation.
Then he reveals the new product. Macintosh presented itself.
Show the benefits
He outlines what Apple is doing differently after demonstrating the product.
How do you distinguish from others? The Big Breakthrough Presentation.
A few hundred slides might list all benefits.
Everyone would fall asleep. Have you ever had similar presentations?
When the brain is overloaded with knowledge, the limbic system changes to other duties, like lunch planning.
What should a speaker do? There's a classic proverb:
“Tell me and I forget, teach me and I may remember, involve me and I learn” (— Not Benjamin Franklin).
Steve Jobs showcased the product live.
Again, using ordinary scenarios to highlight the product's benefits makes it relatable.
The 2010 iPad Presentation uses this technique.
Invite the Team and Let Them Run the Presentation
CEOs spend most time outside the organization. Many companies elect to have only one presenter.
It sends the incorrect message to investors. Product presentations should always include the whole team.
Let me explain why.
Companies needing investment money frequently have shaky business strategies or no product-market fit or robust corporate structure.
Investors solely bet on a team's ability to implement ideas and make a profit.
Early team involvement helps investors understand the company's drivers. Travel costs are worthwhile.
But why for product presentations?
Presenters of varied ages, genders, social backgrounds, and skillsets are relatable. CEOs want relatable products.
Some customers may not believe a white man's message. A black woman's message may be more accepted.
Make the story relatable when you have the best product that solves people's concerns.
Best example: 1984 Macintosh presentation with development team panel.
What is the largest error people make when companies fail?
Saving money on the corporate and product presentation.
Invite your team to five partner meetings when five investors are shortlisted.
Rehearse the presentation till it's natural. Let the team speak.
Successful presentations require structure, rehearsal, and a team. Steve Jobs nailed it.
